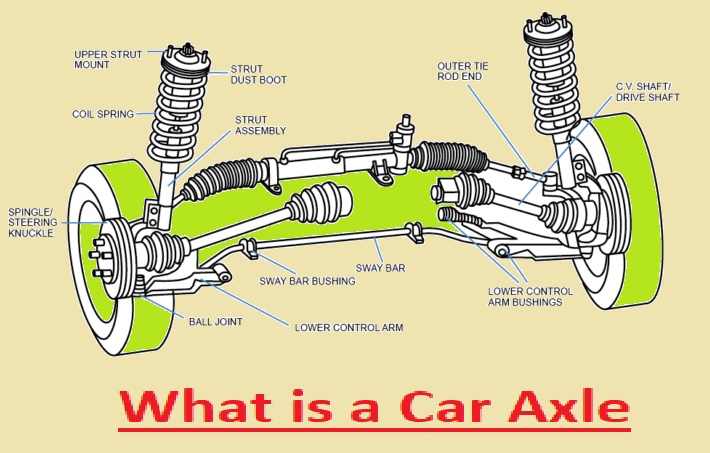
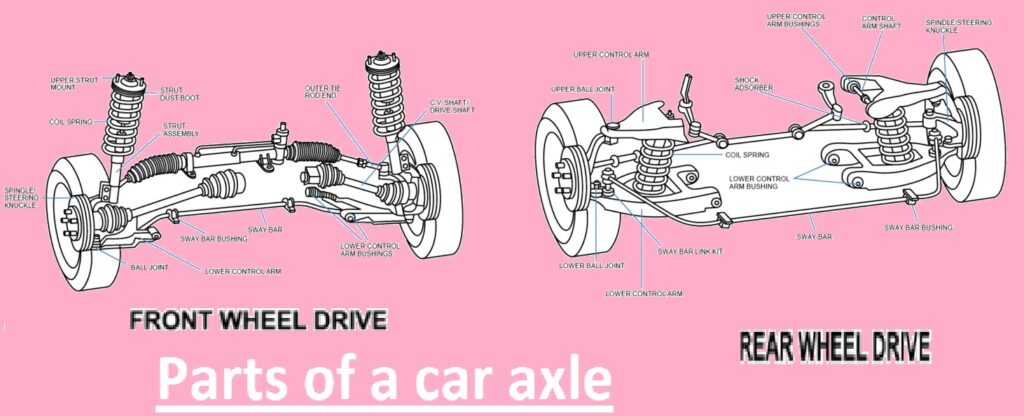
The axle is the main part of the car, which is a rod-like design that makes the connection of wheel pairs for their movement and maintains the wheels’ position. Through the force of the engine axles moving in the car, movement occurs. Axles deliver driving power from the engine to the wheel. In this post, we will cover the detailed features of axles and their importance for driving. So let’s get started.
What is an Axle in a Car?
- The axle is the main part of the vehicle that makes a connection between the drive shaft and causes rotation. Its main operation is to deliver power from the engine to the wheels, which causes vehicle movement.
- Its design is such that it is like a shaft that moves through the middle of the wheel.
- Car wheels are connected and rotate over axle. Axles also manage vehicle weight and passengers sitting in the car.
- wheel-up-down movement is also controlled through the connection of the wheels with the suspension system.
Types of Axle
There are three main types of axles; each performs different operations.
Front Axle
- This axle exists on the front side of the vehicle. This axle is configured with a front wheel. The front axle is made with a design center I like and a circular design on the ends. This design helps axles to easily manage high-load bending forces and torque production braking.
- The front axle controls the steering process and provides support to the front part of the weight.
- It also bears shocks that occur with the help of shock absorbers.
The front axle also has two types that are
Dead Front Axle
- Dead front axles have a fixed assembly and do not move during wheel rotations. These axles provide strength and structural support to the vehicle. The front axle ends provide support to the stub axle.
Live Front Axle
- live front axle like a dead front axle, with the difference that it transmits power from the gearbox to the front wheels and also rotates with the front wheels
Stub Axle
- These axles are connected to the front wheels. Kingpins make connections of stub axles to wheels. They are made with nickel steel and alloy steel that comes with molybdenum and chromium.
- It converts on a pinned pin that is employed for light drive. axle beam eye configured through a taper cotter pin.
- phosphor bronze bushes connected on fork ends of axles that make a bearing area for the kingpin. Forces applied vertically are managed with a steel washer, put on the upper fork and below the axle beam.
Stub axles subtypes
Elliot:
- This axle is connected to the other axle through a fitting in the main axle yoke. After that, the stub axle is configured through the yoke with a kingpin and a cotter.
Reverse Elliot:
- In this axle type, the stub axle comes yoked and configured over the main axle. A reverse Elliot stub axle makes a connection between two axles through a kingpin and a cotter.
Lamoine
- This stub axle comes with an L-design spindle and a yoke hinge. That makes the connection between the axle and the kingpin, and the cotter.
- A cotter also provides locking for the axle in that fixed location. This axle is part of heavy vehicles such as tractors
Reverse Lamoine:
- Reverse Lamoine is an inverted L design.
Rear Axle
The rear axle is configured between the differential and driving wheels for power transmission from the differential to the wheel during driving. This axle is part of the rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
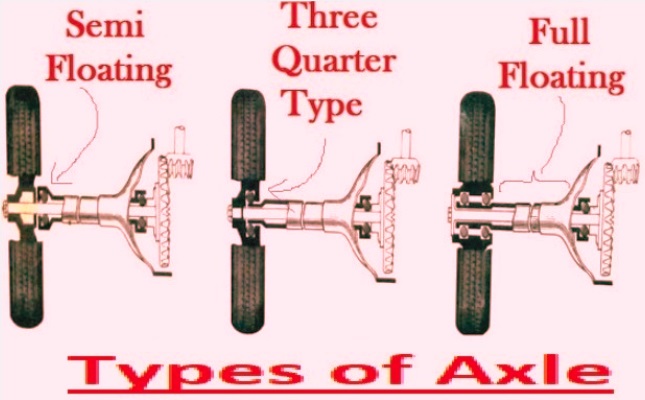
Rear axles have bearings and vertical loads connected to the axle casing with springs that transmit through the bearings to the shaft, causing the wheel to connect to the ground. The main types of rear axles are as
Semi-Floating Axle
- The semi-floating axle comes with a bearing and is connected over the axle and in the axle casing. It supported the total vehicle load. The inner end of the axle is managed with a differential side gear. The wheel is configured directly since the external end is flanged.
- For some axles, the wheel hub is configured to the external axle end.
- Vehicle load shift through casing and bearing that resulted in axle bending. Semi-floating axles are common types since they are low cost and easy to use.
Three Quarter Floating Axle
- In this axle design, a bearing exists between the hub and the axle casing. vehicle weight shift to axle casing. Side thrust and driving torque get at the axle.
- axle connected with hub, which provides driving connection and sets wheel alignment.
- inner end of this axle, like a semi-floating axle.
Full Floating Axle
A full floating axis comes with two grooved balls existing between the wheel hub and axle casing. axle not controlled with bearings on any end. The axle releases the force of the vehicle’s weight. It causes the transmission of torque. That axle is eliminated on the housing without affecting wheel through-nut removal. It is a heavy and costly axle.
How a Car Axle Works
- The main operation of an axle is to transmit rotational power and torque through the vehicle drivetrain to the wheels. that move car forward
- Torque is transferred to the front/back wheels based on different car drives, like front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive.
- For a rear-wheel-drive car, the rear axle gets engine power and torque, causing rotation of the rear wheels.
- For a front-wheel-drive car, the front axle delivers power to the front wheel.
- All-wheel-drive vehicles deliver torque to the front and rear axles, where an automated system is used to get traction.
- differential configured on vehicle axles. That component helps wheels to move at different speeds over corners. causes vehicle movement at optimal speed
Read related guide What is Screw Jack? Features, Types, uses
Main Functions of Car Axle
Engine Torque Transmission
- The main function of the axle is to transmit torque and rotation of the engine to the wheels, which causes the vehicle to drive. The car will not move without the axle transferring rotational energy into tire movement.
- Axles transform the high torque of the engine into traction for the wheels.
different wheel speed
- Axles help wheels to move at different speeds due to differential features. That is important for cornering, where fast rotation is important for the external wheel for bending compared to the internal wheel.
- Differential causes relative motion and provides a strong grip and steering purposes
Vehicle Weight
- Axle structures easily manage vehicle weight, which is a combination of chassis, body, and passenger weight. The high-quality design of the axle provides durable features for handling high dynamic and static weight for a longer time.
- Shock absorbers and sway bars connected to the axle are also managed through the axle assembly.
Driveline Stresses Handling
- Axles have features to manage high torque. during hard braking, and manage twisting forces. Axle shafts manage this torque through supporting bearing control motion. Accurate flexing avoids affecting gear damage and other driveline components when a load occurs.
Bearings and seals housing
- axle support bearing seals that avoid dust particles. Roller bearings provide smooth, low-friction movement of the wheel hub, differential gears, and axle shafts.
Braking and Wheel Mounts
- Axles provide locations for the connection of wheel hubs and brake parts such as drums and discs. Strong mounts provide easy wheel connection, causing the removal of the tire and braking services.
- For accurate transmission of driveline forces, a strong connection between wheels, hubs, and axles is needed.
Different parts of a Car Axle
Spider Gear
- The spider gear helps to transmit torque from the driveshaft to other parts of the gearset and axleshaft; it exists in the differential. It distributes power to provide speed differences of wheels.
Axle Shaft Bearing
- These bearings configure axle shafts, connect with the wheel and differential side gears, and provide easy rotation in high loads.
Drive Pinion Shaft
- This part provides support to drive pinion gears. That comes with bearings that provide smooth power delivery in ring gears and differentials.
Adjuster Nut
- These components control drive pinion bearing preloading. Proper preloading helps to get good gear meshing for transmitting high torque from the engine.
Axle Shaft Housing
- It comes with an inner differential, gears, and bearings and protects from dust and provides lubrication.
Axle Shaft Oil Tube
- It delivers gear oil on the axle assembly, helps proper cooling, and lubricates parts.
Bearing Cap
- It connected with the axle housing, protecting inner bearings in their certain locations with dynamic loads.
Universal Joint Flange:
- This part helps articulation at the external ends of axle shafts where they connect to wheels with suspension movement.
Gasket
- Gaskets works as seals and prevent gear oil from leaking between axle parts such as the housing, axle tubes,, and covering.
Ring Gear
- The ring gear cover differential carrier, configured to drive the pinion gear, causes engine power. After that, torque is delivered to the spider gear.
Side Gear
- This part exists in differential and is configured on each axleshaft. Power move from the spider gears into the side gears causes the rotation of each axle shaft
Differential Carrier
- This part comes with different differential components, such as a spider, ring, and side gear. that provide motion between outputs and manage wheel speed factors
Spider Gear Shaft
- . This component supports the spider gear in the differential carrier and causes the rotation of the axis.
Drive Pinion Gear
- The drive pinion gear exists on the endpoint of the driveshaft and gets power from the transmission and engine to the axle structure with the ring gear.
Read related guide What Is A Car Fender & difference from Bumper?
Conclusion
The axle is a vital driveline part that helps to make a connection between the wheels with the transmission and differential. It transmits power to the four wheels from the engine and helps to move at different speeds.
Axles needed to rotate uniformly with high torque and support the vehicle’s weight. It manages different designs of drive, like front, rear, and all-wheel drive.
Through getting an idea of axle parts and accurate types, we can make safer, more reliable operation of the vehicle.