Welding is a process that operates through using pressure, heat, or both for making a connection of two metallic components. Welding has different types, such as stick welding and TIG welding, that work with different flame types.
Welding flames provide heat to the metal and cause the welding process. Welding flames are the main part of the welding process since it is with flame heat generated that causes the welding process. In this post, we will cover the detailed features of welding flame types and related features.
What is Welding Flames
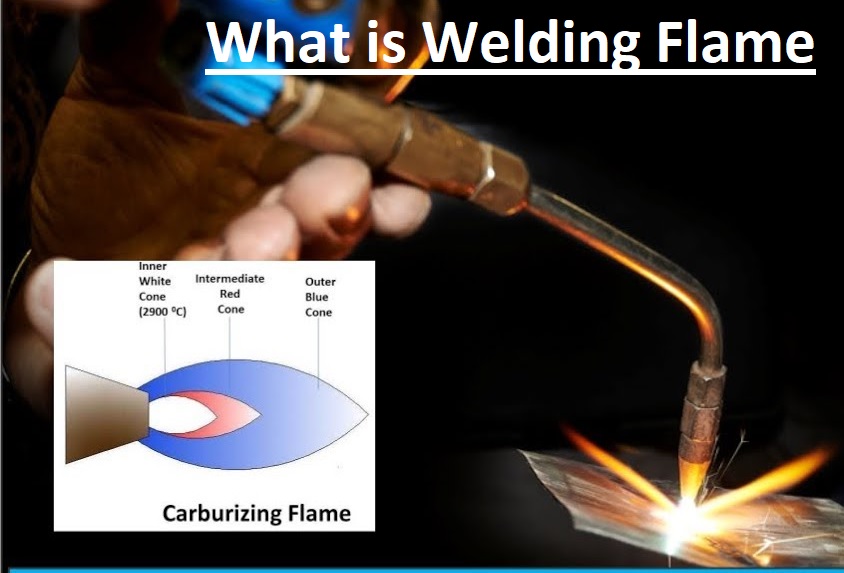
- Welding flame is the heat produced when the welding process is performed. A flame is produced through gases like oxygen, acetylene, or natural or propane gases.
- High-intensity flame is applied for melting metals and making their connections. Flames come in different colors, sizes, and structures according to welding types and gases used.
- Welding flames provide heat to metal and provide a controlled welding process.
Flame Control’s importance in Welding
- Flame control provides quality welds for the welding process. A proper flame is the result of constant heat generation, enhances weld metal quality, and reduces the effect of oxidation.
- Accurate flame control helps to maintain the required temperature. It does not cause metal contamination and makes a durable weld.
- If not, it has improper flame control as a result of bad welds. Improper setting causes porosity, weak joints, and metallic cracks; these faults cause a low-quality structure.
Welding Flames types
Read our related guide What Is Welding Bead? Features, Uses, & Types
Oxy-Acetylene Flame
- Oxyacetylene flame crests through acetylene gases, burning with oxygen.
- a flame made through a torch that comes with separate parts, where acetylene gas and oxygen exist.
- Oxygen is configured over high pressure and acetylene at low pressure. This flame has varying features and adjusts for different output heat values, such as cool flame to high-temperature flame, to perform cutting and high-thick metallic welding.
- Oxyacetylene flame is also employed to weld metals such as magnesium, cast iron, and aluminum.
- Flame also comes with different color combinations, such as blue and yellow, according to the gas mixture.
Oxy-Fuel Flame
- An oxidizing flame is produced through a low amount of acetylene in a natural flame and a high amount of oxygen.
- This flame has a higher temperature than a natural flame and comes with two zones.
- The inner zone causes bright color, and the temperature value is 300 degrees.
- The outer flame is blue in color. that is employed for welding copper alloys, brass, and bronze.
- Oxy-fuel flame is employed to perform ferrous and non-ferrous metal and welding, also performing as brazing and soldering.
- It can be employed for closed spaces and low cost.
- The flame’s temperature and color design vary according to gas pressures, tip, and welding methods.
Propane Flame
- A propane flame is generated through burning propane gas. That flame is the result of a torch that has a propane gas supply. A blue-colored flame is generated, and it causes high heat, which is good for thick material welding.
- propane flame used for brazing and welding and used for causing a stable flame and high heat control
- It is lower cost than other types. Propane flame is used for industries like soldering, brazing, and lighting.
Natural Gas Flame
- This flame is generated through natural gas burning, and this flame is produced through a torch that has a hose providing natural gas.
- A blue flame has a blue color, with low heat output, and is best for applications where accurate heat control is needed.
- Natural gas flame is part of the welding and brazing process since it has features to make a stable flame with high heat control.
- It is a lower-cost option than other types. Natural gas flame applications were heating and lighting applications.
- The temperature of the flame changes according to pressure and gas flow.
- Natural gas flames need ventilated areas since, during their applications, carbon monoxide gases and nitrogen oxides are produced, which are hazardous to our health.
- A natural flame occurs when an acetylene flame is generated through the wing expansion of the inner core.
- A natural flame occurs when an acetylene flame is generated through the wing expansion of the inner core. For reducing the acetylene flame, the oxygen valve is open, and a low quantity of oxygen is obtained.
- A natural flame does not have white current, but a minor acetylene stream with 1.6 to 3.2 mm, which causes the flame to not be oxidized and sets that employed for welding functions
Welding Flames Features
Read our related guide What is Undercut in Welding? Causes & Prevention
There are different features of welding flames that define its operations.
Temperature
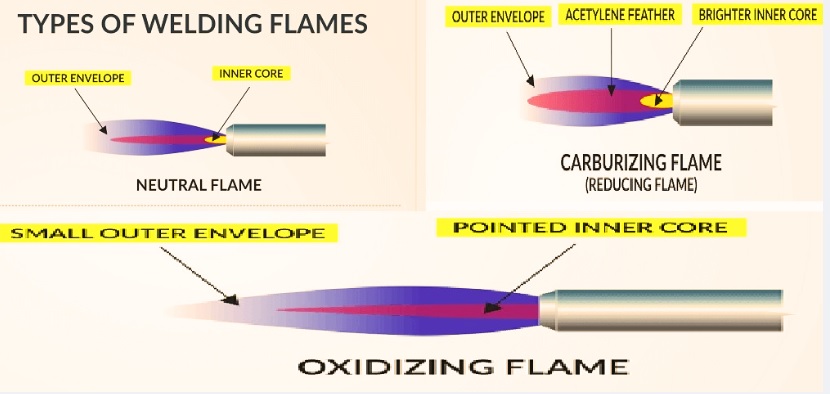
- Different temperature values exist for each flame type. Flame temperature is defined based on gas mixture and gas pressure. A natural flame provides the required temperature value for welding and oxidizing flame. A cool temperature with a carburizing flame is hot.
Flame Color
- Flame color is different according to the gases used and the mixture of gases. Oxyacetylene flame is blue, purple, and yellow. The oxy-fuel flame color is blue; propane is also blue.
Shape
- Flame shape based on the tip and gas pressure. A natural flame comes with a cone-like design, an oxidizing flame has a pointed design, and a carburizing flame is bushy-shaped.
Size of flame
- Flame size is based on gas pressure and tip used. Natural flame, small size and carburizing flame, larger dimensions and oxidizing flame very large
Brightness
- Flame brightness based on gas types and their mixture. A neutral flame shows high brightness, a carburizing flame shows low brightness, and an oxidizing flame low.
Combustion process
- Flame combustion based on ongasesand their mixture. A neutral flame comes with complete combustion, and a carburizing flame causes incomplete combustion and over-combustion for an oxidizing flame.
| Aspect | Neutral Flame | Carburizing Flame | Oxidizing Flame |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen–Fuel Ratio | Fuel = Oxygen (balanced) | Fuel > Oxygen (excess fuel) | Fuel < Oxygen (excess oxygen) |
| Temperature | ~3,200°C | ~3,000°C | ~3,500°C |
| Flame Color | Clear, well-defined inner cone | Blue inner cone and luminous secondary feather | Short, intense bluish-white inner cone with faint external envelope |
| Application | Mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum | High-carbon steel, cast iron; metals benefiting from carbon enrichment | Cutting, brazing, copper alloys |
| Effect on Weld | solid welds without impurities, Minimal oxidation; clean, | added carbon into the weld | oxidized, brittle welds if not properly controlled |
| Main Characteristics | produces uniform results | Lower temperature, reducing flame | Hottest flame, intense flame |
| Advantage | general-purpose flame | carbon-enrichment welding | cutting operations |
| Limitation | Few limitations | faces over-carburizing | risk of oxidation |
What is the color of Flame mean?
Read our related guide Mig Vs Tig Welding: Basic Differences
Flame color indicates chemical composition, applications, and temperature. The accurate color of a welding flame makes a quality weld, and improper color causes error. The meaning of flame color is as
- Blue color means a neutral flame that is preferred for general welding.
- The white color is an oxidizing flame that is high temperature and if not handled properly, can be hazardous.
- orange or yellow, the flame is reducing that with high carbon and preferred for metals where reducing conditions are needed
Type of Gases for Flame
- Acetylene is a commonly used gas for welding flames. MAPP and hydrogen are used as replacements for acetylene.
- The acetylene triple bond helps to strongly connect carbon atoms.
- as compared to other gases that break at ignition temperature. But acetylene releases energy, and so it helps to provide high temperatures.The
- oxidizing features of acetylene are also less than other gases. but provide easy ignition
- MAPP liquified petroleum gas mixture of propane and acetylene. It is delivered in a smaller container than standard acetylene, has a high ignition temperature, and has high pressure.
- The flame of MAPP has a lower temperature than acetylene flames.
- It is not preferred for steels but is used for aluminum metals as well.
- For aluminum welding, hydrogen is used, since for MAPP hydrogen flames, the temperature gets low and the pressure gets high.
Safety factors for welding flame
Gas handling
- Gas handling and proper storage main safety factors. Store gas in a ventilated area; avoid heat. proper maintenance, leak check, and fitting
tool handling:
- Accurate handling of the welding process. Welding tools are needed to check for faults and cracks, and must maintain the structure according to the manufacturer’s requirements.
- If any damagedtool replacedit
staff safety
- Before working with welding, use safety measures, like gloves, welding helmets, and protective assemblies.
- Since fumes and gases produced during production affect eyes and respiratory
properly ventilated area
- Perform the welding process in a properly ventilated area that avoids fume inhalation. Ventilation releases fumes and gases accurately.
FAQs
What welding gas produces purple flame
- Oxyacetylene flame causes purple gas welding that has high temperature and welds different metals.
- This color helps easy control of flame. Oxygen and acetylene gases are mixed for an oxyacetylene flame. that passes in separate hoses for the torch. Oxygen pressure is high, and acetylene has low pressure.
- blue flame employed for welding and purple flame carburizing
Read our related guide What is Porosity in Welding? Causes, Types, Effects and Solutions
Why are welding flames colored blue
- Welding flames are blue in color since they have carbon monoxide. Blue flame is the normal welding color due to the oxygen-acetylene mixture.
- Blue color generated through oxygen reaction with acetylene gases causes heat and a blue-colored flame.
- Blue flame is a natural flame and part of a common welding process. It heated welding temperature and worked in controlled conditions.
What are the flames types of oxy-fuel welding
- Commonly used flame types are oxyfuel welding, 2nd is carburizing flame, and 3rd is neutral flame.
- A neutral flame is commonly used for the welding process. It is produced with acetylene, a mixture of fuel gas and oxygen.
- A carburizing flame generated with acetylene causes a yellow-colored flame. It performs hard facing, brazing, and metal preheating.
- An oxidizing flame is the result of an oxygen mixture that causes the flame to be blue or white. It performs post-welding cleaning that removes slags.
What is the quality flame for welding?
- A commonly used gas welding method is oxy-acetylene welding. that is made with oxygen and acetylene generated through a high-temperature flame of about 3,500°C, and used for different metals
Which flame is preferred for brazing?
- A neutral oxyacetylene flame is employed for the for welding process. Silversoldering for metals commonly uses a flame. A neutral flame is preferred for oxyacetylene cutting.
Why is a neutral flame preferred for welding?
- It produces clear and bright fumes that result from proper combustion. A neutral flame is employed for welding of metals, mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. oxidizing fumes made with high oxygen