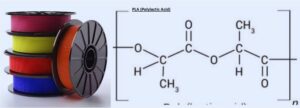
Polylactic acid’s other name is PLA, which is a thermoplastic monomer obtained from renewable, organic sources like cornstarch or sugarcane. The use of biomass resources makes PLC have different features than other plastics that are made through distillation and polymerization processes.
PLA also made with use of tools like petrochemical plastics and making PLA production low cost option. PLC is the 2nd bioplastic and comes with the same features as polypropylene or polystyrene. In this post we will cover details, features, and related factors. Let’s get started.
What Is PLA (Polylactic Acid)?
- Polylactic acid, also called poly or polylactide,is a plastic material. It is made with the use of ring-opening polymerization of lactide. the cyclic dimer of repeated base units. PLC is mixed with other polymers. PLA is biodegradable and works longer, based on the production technique, additives, and copolymers, and is also used for compostable products.
- It also has a higher consumption volume than other bioplastics in the world, and its share is ca. 26% of total bioplastic demand.
- Either its manufacturing is becoming fast, or it is less important than conventional commodity polymers such as PET or PVC.
- It is a commonly used plastic filament material with FDM 3D printing since it has a low melting point, high strength, and low thermal expansion and also provides low heat resistance without annealing.
- The term polylactic acid is commonly used. It does not support IUPAC standard nomenclature, which is poly.
Fabrication Process
- PLA objects are made with use of the 3D printing process, casting, extrusion, injection molding, machining, and solvent welding.
- PLA is used as feedback material for desktop fused filament manufacturing with 3D printers, like RepRap printers.
- PLA can be made as solvent welded with the use of dichloromethane. Acetone also reduces the hardness of the PLA surface and makes it sticky in nature without dissolving, which helps to weld other PLA surfaces.
- PLA-printed solids are covered in plaster-type molding materials that are burned in a furnace, resulting in a void filled with molten metal. That’s called lost PLA casting, which belongs to investment casting.
PLA Types
- It has a lactic acid nature, so it comes with different types of polyactide. That comes with poly-L-lactide, that is originates from the polymerization of L-lactide.
- PLA, also made with different biomass materials like cornstarch or sugar, can also provide different features with the combination of other metals.
- Different types of PLA are as
Wood Filaments
- PLA is mixed with woods like bamboo, coconut wood, pine, and cedar. It is used for providing PLA-printed furniture creation with a natural look.
Metal Filaments
- Different metals such as brass, bronze, copper, and iron are mixed with PLA that makes printed components stronger and glossy.
Other Filaments
- PLA is also mixed with other materials such as carbon fiber, conductive carbon, and also coffee. PLA filaments also provide different color features.
PLA Properties
PLA can be soluble in different solvents such as dioxane, hot benzene, and tetrahydrofuran. Physical and mechanical features differ based on polymers, such as amorphous glassy polymers to semi- or high-crystalline polymers that have a glass transition value of 60 to 65 and a melting temperature of 130 to 180 degrees, and a tensile modulus value of 2.7 to 16 GPa.
- Heat-resistant PLA has features to handle a temperature of 110 degrees, and the melting temperature increases by 40 to 50 degrees, and the heat deflection temperature is 60 degrees to 190 degrees. With that, it has a physical blend of polymer to PDLA.
- The addition of nucleating agents or forming composites with other materials can vary the mechanical features of PLA through the annealing process.
- the basic mechanical features of PLA lie between polystyrene and PET and have same features as Pet with low maximum continuous temperature
- PLA is good to use for 3D printing since it has high surface energy and is solvent-welded with the use of dichloromethane, and acetone softens the surface of materials, and it is sticky in nature without dissolving, so it provides easy welding with other PLA surfaces.
- Ethyl acetate operated as an organic solvent, dissolving PLA and increasing its solution features for removing PLA printing supports.
- Propylene carbonate and pyridine also are solvents with lower features than ethyl ethylacetate and propylene carbonate and are less safe and release certain bad fish-like smells.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Density (g/cm3) |
1.27 |
|
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
59 |
|
Elongation @ Break (%) |
7 |
|
Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
3500 |
|
Shear Modulus (MPa) |
1287 |
|
Flexural Strength (MPa) |
106 |
|
Rockwell Hardness (HRA) |
88 |
|
Glass Transition Temperature (°C) |
55 |
|
PLA Melting Point (°C) |
165 |
PLA Manufacturing Methods
- There are different methods used for making PLA with provide high molecular rate. The basic components used for making PLA are lactic acid and cyclic diester. Different processes used for PLA manufacturing are as
Ring-opening polymerization of lactide
- The common technique used for PLA is ring-opening polymerization of lactide, where different catalysts are used in solution. The metal-catalyzed reaction helps to cause racemization of PLA that minimizes stereoregularity features compared to biomass starting materials.
Direct condensation of lactic acid monomers
- We can also make PLA with the use of direct condensation of lactic acid monomers. This process is performed at below 200 degrees, where entropically based lactide monomers are made.
- This process produces water equivalent to the esterification step. Water is removed with use of a vacuum to promote polycondensation and get a high molecular rate.
- High molecular rates are obtained with crystallizing crude polymer through melt. Carboxylic acid and alcohol end groups of amorphous parts of solid polymers provide a molecular weight of 128–152 kDa.
Polymerizing a racemic mixture of L- and D-lactides
- Through polymerizing a racemic mixture of L and D lactide, it is good to synthesize amorphous poly-DL-lactide.
- Stereospecific catalysts cause the formation of heterotactic PLA that shows crystallinity features.
- This crystallinity feature is regulated by the ratio of D to L enantiomers and also the type of catalyst used.
- The 5-membered cycile compound lactic acid O-carboxyanhydride (lac-OCA) is used for academic covering as compared to lactic acid and lactide.
- This mixture does not make water as a co-product and has higher reactive features than lactide. PLA is also biosynthesized, and lactic acid is also mixed with zeolite to make a one-step process that occurs at a temperature that is less than 100 degrees.
Advantages of PLA
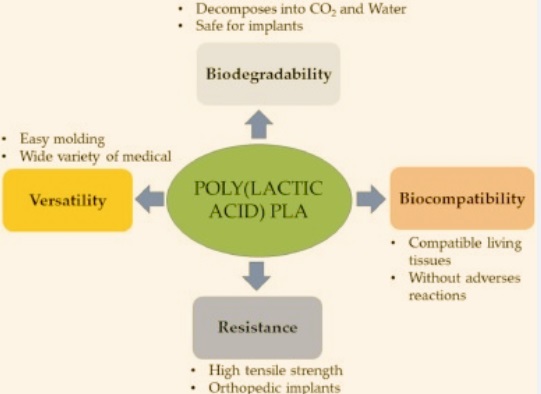
Biocompatibility:
- PLA is not toxic for us, and it makes a connection to our body without any bad effects. The decomposition products of PLA are also not toxic. It degraded into less hazardous lactic acid. It is used for stents and sutures that have features to break down in the body for a long time.
Low-Energy
- PLA gets lower energy for production than other petroleum plastics since it has a relatively low melting point of 165 degrees. The polymerization of PLA also uses 25 to 55 percent less energy as compared to other petroleum-based polymers.
Mechanical Strength
- PLA provides good strength and stiffness at room temperature but does not work well for abrupt effects of loads.
Food Safety
- PLA is nontoxic and also safe according to the FDA.
Compostable:
- PLA has a compostable nature since it is processed with certain temperature and pressure conditions that come with composting facilities.
Disadvantages of PLA
Hydrophobic Material:
- Hydrophobicity is a good feature for some sutures that make negative in vivo factors like swelling.
Low Thermal Resistance:
- Its low melting temperature makes it easy to process. PLA is not used for temperatures more than 50 degrees since it has a low glass transition temperature of 55°C.
Low Toughness:
- PLA is brittle in nature and breaks but does not bend when force is applied and does not handle impact loading.
High Permeability:
- PLA is permeable in nature to gases and water that can flow through materials.
FAQS
Which PLA Is the Strongest nature?
- PDLA and PLLA are semi-crystalline and come with strong intermolecular bonds than amorphous PDLLA. The strongest type of PLA is PDLA and PLLA thta has same features with different molecular designs.
- PLA+ is PLLA that has some additives to increase its toughness and strong type of PLA in 3D printing applications
What Is the Difference Between PLA and PLA Plus?
- PLA plus or PLA+ are tougher nature than PLA, that is not brittle like PLA. The accurate chemical difference between them based on the PLA plastic company. Different additives are used for standard PLA and called PLA Plus
Is PLA supported with 3D Printing?
- PLA is supported 3D printing, basically PLA is a common type of plastic that used for FDM sinca can be molded in differnt shapes
How Is PLA applied in 3D Printing?
- PLA works asa filament for 3D printing, PLA raw materials is made in different plastic filaments with a diameter range of 1.75 to 2.85mm.
- This filament is put into a heated extruder that applies force through molten plastic in the nozzle, to make components of layer by layers.
- PLA not need heated print bed and the extruder temperature is in the range of 190 to 200 degrees.
- PLA filament is easy to use and comes with low features for warping at time of printing method