A milling machine is commonly machine in industries. It has different types that perform different functions. Milling machines are used for materials removal on materials with the help of rotary cutters. The removal process occurs in the line tool axis, that called milling so it is called milling machines. In this post, we will cover details, features and related factors. let gets started
What is a milling machine?
- The process that removes materials from the working component with the use of rotary cutters is called milling.
- In this process, pressure, cutter head speed, and feed direction are accurately set for material removal.
- Basically, the milling machine is the part of the tool that removes materials using a multiple-point cutting tool on the surface.
- Milling cutters move with high speed, and their cutting edges remove material quickly.
- Milling performs different operations, like small parts or larger materials.
- • The The milling process is performed with the use of different tools; the invention of computer numerical control also revolutionized the process.
- Milling machines come with vertical machining centers (VMCs) or horizontal machining centers (HMCs).
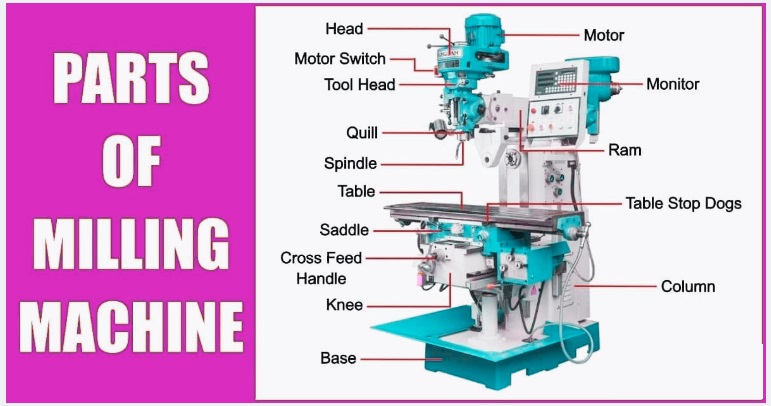
Main Components of a Milling Machine
A milling machine comes with different parts, and each performs a certain task. All milling machine parts are explained here.
Base: The
- base: the main part of the milling machine, and the complete structure of the machine is configured on the base. It is made with rigid materials such as cast iron. The base handle machine weight absorbs the shock produced during the milling function.
Column:
- • The column is the frame where moving components of the machine are connected. It manages the driving process of the machine.
Knee:
- This part of the milling machine lies on a base that manages the complete weight of the working table. The knee comes with a handle to handle weight through guideways and screwing. It has a connection with the column for providing support and vertical motion.
Saddle:
- • The saddle makes a connection of the working table to the knee. The saddle makes a connection of the knee through the guideways. that provides 90 degrees of motion of the working table on the column
Spindle:
- spindle configured on the cutting tool on the machine. For multi-axis milling machines, the spindle provides rotary motion.
Arbor:
- It is a tool adapter that provides side cutter support. It configured the spindle.
Worktable:
- This part of the milling machine holds the working materials. The workpiece is held on the working table through clamps. The table provides longitudinal motions. Multi-axis milling machines come with rotary tables.
Headstock: The
- • The headstock holds the spindle and makes a connection with the remaining parts. The spindle moves through motors that are connected in the headstock.
Overarm:
- Overarm manages spindle weight and arbor structure. It is connected to the upper part of the column and is also called the overhanging arm.
Milling Machine Working Principle
- Milling is a cutting process operated through a milling cutter for removing materials on a working component.
- The milling cutter is a rotary cutting tool that comes with different cutting points.
- as compared to the drilling process, where the tool operates along the rotation axis, and the milling cutter moves 90 degrees to the axis for providing the cutting process.
- When the milling cutter passes through working materials, the cutting edges of the tool cut inside and outside material and remove materials from components.
- • The cutting process involved shear deformation, and materials push off the working component in small parts and were removed larger materials.
- • The milling process removes materials by separating small parts. that is performed with a cutter, normally involving three phases
- Speeds and feeds can be different based on variables. speed where the component passes through the cutter, called the feed rate, which is measured with distance per time and sometimes measured as distance per revolution.
- Normally, the milling process involves two types.
Face milling
- the cutting process performed at end points of milling cutters. Face milling is employed for cutting flat surfaces in working components and also cutting flat-bottomed cavities.
peripheral milling
- • The cutting process occurs over the the cutter circumference; as a result, the cross section of the surface gets the cutter shape. In these conditions cutter blades remove materials in working components.
- Perpendicular milling is good to use for cutting deep slots and gear teeth.
Milling Machine Technical Parameters
There are different factors involved in the working of milling machines. We must know these factors. These are
Rotational Speed:
- rotational speed, where the cutting tool rotates and is measured with rotations per minute and denoted with n
Tool Diameter:
- Diameter measured in millimeters and denoted with dc. Larger diameters provide high material removal. For high accuracy, a small cutter is used.
Cutting Speed:
- Cutting speed is the linear speed of the tool that is denoted with withVc and the measuring unit is meters per minute (m/min).
Feed Speed:
- Feed speed is the rate of motion of the cutting tool in the working component. It is denoted with Vf, and the measuring formula is
Vf = Ff x n; Ff is the feed per revolution.
Depth of Cut:
- It defines how much depth the tool cuts in the z-axis; larger depths provide high tool wear.
Different Types of Milling Machines
There are different types of milling machines, and each type has its own uses.
Vertical Milling Machines
- The vertical milling machine comes with a spindle axis at 90 degrees. The cutting tool passes deeply into the working component for cutting and drilling. Vertical machining exists in two types: bed mills and turret mills. that comes with longer cutting parts
Horizontal Milling Machines
- The horizontal milling machine comes with a spindle axis in the horizontal plane. Cutting tools cut materials from the side rather than the upper part. This machine comes with a rotary table that cuts at some angle.
- Cutting tools in a horizontal milling machine are thick and small in size.
Universal Milling Machines
- This machine comes with horizontal and vertical features. It has a working table rotatable at 90 degrees and gives access for planes.
3-axis Milling Machine
- The 3-axis milling machine is commonly used that used for cutting at 3 axes: x, y, and z. These machines are low cost and easy to use. It also needed a low repairing process since it has a simple desig
4-axis Milling Machine
- This machine moves in 3 linear axes and a rotary axis. The rotary axes are a, b, and c. a is x b is y and c is z axis. 4-axis milling machines are used for making complicated designs since they provide angular motion for cutting tools.
5-axis Milling Machine
- These machines come with three linear axes and 2 rotary axes. It makes complex designs with speed for bulk production since it makes a simple spindle axis.
Fixed Bed Milling Machine
- • A fixed bed milling machine comes with a static bed connected with a frame. Knees and saddles are not variable in this machine. the fixed bed milling machine used for cutting purposes. It also has easy maintenance features.
Knee-Type Milling Machine
- It is a vertical milling machine that is configured with a worktable on a moving casting that is a knee. Knees move vertically in the z-axis. that help to set the vertical position of the working table. Knee mills are good to use for drilling purposes through a milling machine.
Planer-Type Milling Machine
- The planner mill is an easy design used for cutting the surface of a working component at 90 degrees to the machine tool axis. This mill is commonly used for wood cutting for finished timber.
- Planer mills work easily and have basic design and assembly.
main milling machine functions
There are different functions milling machines perform. that are explained here:
Form Milling
- The form milling machine makes curved and straight lines on the working component. It also makes a completely curved contour. The curves made with milling cutters are of concave and convex design.
Peripheral Milling
- It comes with a milling cutter in parallel with a working component that has a 90-degree design. A milling cutter comes with single-point or multipoint cutting edges on the sides. side removes materials at the upper part of the materials.
Plunge Milling
- • A plunge mill gives materials to the milling cutter at the z-axis for deep plunges into working materials. When the cutter is at the required depth, it moves back to the z-axis and sets to the x and y axes and again plunges into the materials.
Saw Milling
- Sawmilling is used for cutting logs to make lumber. In this milling process a circular or linear toothed cutter is used.
Groove Milling
- Groove milling makes slots and grooves at different dimensions of the working component. It used a cylindrical cutting tool that plunges materials to a shallow depth and removes materials at the tool side.
Thread Milling
- It is a niche mill that makes internal and external threads in working materials. Threads cut with single, dual, and three-point cutting tool rotation
Cam Milling
- It uses a universal dividing head for vertical design to make cams. spindle axis and cam mill axis parallel with each other
Gear Milling
- It cut toothed gears in round working materials. The cutter removes materials to make a cavity between 2 gear teeth. The working materials rotated with one gear space. The cutter removes another cavity. working continuously until a complete gear is made
Angle Milling
- Angle milling is used for designing different angles on working materials. Its other name is angular milling. angle of surface based on contour of milling cutters
Profile Milling
- Profile milling is used for finishing and semi-finishing working materials. It is used for removing a lesser quantity of material on a working component to make flat surfaces.
Side Milling
- This process makes flat surfaces on the side of the working component. The cutting depth varied with the vertical feed screw on the table.
Slab Milling
- This process makes flat surfaces on materials. It is used for finishing working materials and minimizing the thickness of the material. Slab milling uses a horizontally directed cutting tool having different toothed edges. It is also called plain milling.
Up and Down Milling
- This process provides cutting tool rotation in the same way as feed moves. It is also called conventional machining. The down milling defines cutting tool rotations in the reverse direction of feed. Down milling provides parts finishing.
Face Milling
- Face milling operates cutting tools set at 90 degrees to working materials for removing materials. Cutting tools remove low materials for making flat designs. It uses both single-point and multipoint cutting tools. It used to make smooth parts.
End Milling
- It uses a cylinder cutter having toothed edges for surface preparation of materials. The cutter has the same direction as the drill bit. A drill bit moves in an axial direction, and an end mill moves sideways for removing parts from working materials.
Gang Milling
- In this process a single arborist manages different cutting tools. The cutters perform milling operations or are lonely set to perform different functions.
Straddle Milling
- Straddle milling uses two end mills configured on 2 different sides of a single arbor. that has features for working on 2 different material surfaces at the same time. the spacing collar used for setting space between two cutters.