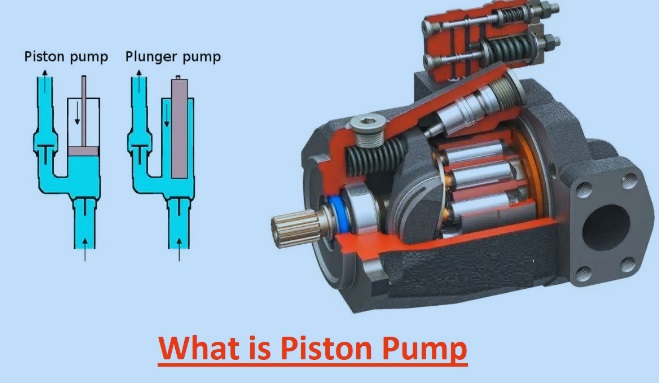
A piston pump is a positive-displacement pump type. In this pump, a piston reciprocates a high-pressure seal. Piston pumps are used for gas compression and liquid movement. It operated with a different pressure valve range. It can manage high pressure without affecting the flow rate.
Without using it for fluids and gases, Piston pumps are also used for viscous fluids and media that have different solid components. Common applications of piston pumps are where high constant pressures are needed and in irrigation systems for water delivery.
What is a piston pump?
- A piston pump is a type of positive-displacement pump that is commonly seen in industries where constant and accurate fluid flow is needed.
- This pump operated with a reciprocating movement that was provided by cylinders through pistons.
- The working of a piston pump is based on a valve, cylinder, piston, and drive system.
- cylinder made of steel or cast iron, since it handles high pressure.
- piston fitted in a stroke through low leakage that helps easy fluid movement.
- Valves control fluid flow in and out of cylinders to control reverse flow. In this unidirectional movement, fluid occurs.
- piston moves through different sources like hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric
- The piston pump comes with many features, like high effectiveness, providing accurate flow rates and pressure, and handling different pressures and fluid viscosities.
- It is normally seen in applications where hydraulic systems with oil and gas generation exist and water treatment systems
- It also has some limitations, such as mechanical wear that occurs and needs maintenance for accurate working.
Types of Piston Pumps
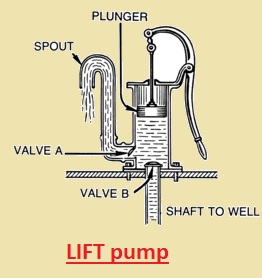
LIFT pump
- In this type of piston pump, water is drawn through the upstroke piston through the valve into the lower side of the cylinder.
- For the downstroke, water moves through the valve set in the piston into the top area of the cylinder.
- For the next upstroke, water releases from the top area of the cylinder through the spout.
- This pump is limited by the water height, which is controlled by the air pressure acting in opposition to the vacuum.
Force pump
- The upstroke of the piston moves water through the inlet valve to the cylinder for this pump type.
- Water is released through the outlet valve to the outlet pipe on the downstroke.
- Pistons are categorized based on single-acting and single-effect features, where fluid is pumped through a single piston face and an active stroke in a single direction.
- double acting and double effect, fluid pumped with both piston faces and stroke work in both directions
Reciprocating Piston Pump
- It is a simple pump type that has one or more pistons that move for fluid flow in the cylinder. This piston pump is single-acting, where fluid moves out in one direction, or double-acting, which moves fluid through both piston strokes.
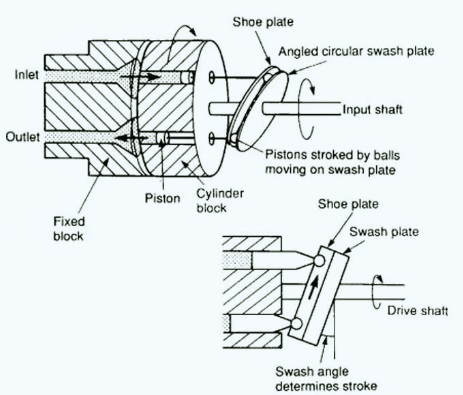
Radial Piston Pump
- In this pump, the piston moves outward in a radial way from the middle of the cylinder block, operated with a cam process.
- It makes different volume chambers that cause suction and discharge fluids.
- Radial piston pumps provide high efficiency with a compact design and are preferred for high-pressure systems.
Plunger Pumps
- Plunger pumps have plungers that move back and forth in a stuffing box, which increases or reduces fluid volume.
- This design is used for high pressures since a static seal exists in the pump; it is the reverse to the piston design, where the seal moves in a hollow chamber.
Features of Piston Pump
The main features of a piston pump are as follows:
Positive Displacement Working
- positive displacement working principle of this type of pump, where a fixed volume of fluid is displaced through a single stroke of pistons.
- Through this process ,fluid accurately moves with consistent features without affecting the pressure of the system.
High Pressure
- The piston pump has features for producing high pressure and is preferred for applications where high pressure is needed, like the hydraulic system of heavy machines or high-pressure cleaning.
Variable Flow Control
- Its design has variable flow control features so we can adjust the flow rate according to process demand.
- It increases efficiency and flexible features with control through fluid movement in different processes.
Fluid Compatibility
- There are different fluids that exist, like corrosive chemicals, viscosities, and abrasive slurries that are supported with piston valves. so we can use this valve for different industries like oil and gas and also for food processing.
strong structure
- It is made with different durable materials like cast iron, steel, or alloys that help to operate the pump in high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, and also work well for corrosive conditions.
- They work for a longer time with less repairing and damage.
Low Leakage
- Its design is such that it has low leakage between the cylinder wall and piston for providing easy movement without losses of pressure.
- It has strong and quality seals for maintaining system quality and reducing leakage.
Maintenance
- They needed regular maintenance for long-term working, but it’s designed such that the maintenance process is easy and does not require certain tools for performing maintenance.
- So use of lubrication and checking valve seals with some parts replacements for damaged parts can be performed instantly.
- The working life of a valve increases through proper care and handling that reduces downtime.
Automation
- The piston pump is easily connected with the automated process due to the use of advanced control systems and automation technologies.
- They are preferred for different conditions since they provide good productivity and do not require manual operations.
- These features make the pump flexible and a proper solution for industries for handling fluid flow and high pressure and provide durable features.
Piston Pump Structure
- piston pump fixed on a strong base or framework. Their supporting structure comes with mounting points where drive motors or actuators and other components, like filters and pressure gauges, are connected.
- All components are configured in the proper way for easy working of the piston pump and cause uniform fluid flow for different processes used in industries where fluid transfer is needed.
Diaphagm vs Piston Pumps
Diaphragm pumps
- The diaphragm pump comes with a flexible diaphragm with a check valve rather than a piston for fluid movement. The reciprocating movement of the diaphragm causes fluid to go in and out of the pump.
- Its controlling setting helps to get constant pressure or constant flow.
- Teflon or polypropylene is used for making a diaphragm that helps to move water-based and solvent coatings.
- This pump easily works for high pressures of about 500 psi and also high volume flow.
- These valve handles have abrasive paints that are viscous and coating without chance of sticking, unlike piston valves. The purpose of the diaphragm to separate the fluid chamber from the pumping process
- Their design provides uniform fluid movement based on the design that is needed for accurate paint metering and spraying.
- Some diaphragm pump types do not use electrical power since they are air-operated, and compressed air operates them.
Piston pumps
- This pump uses a reciprocating piston diaphragm for fluid movement. The piston moves in the cylinder.
- Inlet and outlet valves help fluid to enter and exit the cylinder.
- The piston pump has high-pressure features like 1500 psi or more.
- It provides high pumping speeds for high flow rates. with consistent, pulse-free flow.
- Seals of pump control inner leakage for constant flow.
- Fluids make a connection with the piston and valve to control dust or impurities away from the crankcase.
- If the pump operates at high speeds, flow rates increase, and pressures are based on piston area and force applied.
- Piston pumps easily control medium- to high-viscosity fluids.
- It needed proper maintenance, such as seal replacement, more commonly than diaphragm pumps.
- Pistons can be damaged with time due to abrasive coating use, requiring filtration for handling abrasive paints to manage wear.
- It’s causing a leak that needs proper maintenance.
- It is used for accurate paint metering and sometimes dispensing.
- Small pistons produce high pressures, and larger ones give high flow rates.
Piston and Plunger Pumps
| Piston Pumps |
Plunger Pumps
|
| It is a high seal reciprocating with a piston in the cylinder. |
High-pressure seal is static. The plunger slides in the seal, helping the pump to work for higher pressures.
|
| Inlet design pressure range is 8.5psi to 40psi |
Inlet design pressure of 60-70psi
|
| used for short duty cycles where a larger pump operates slowly. |
Good for continuous operation when run slowly.
|
| Inlet values are mechanically operated. |
it needed flooded suction or a higher inlet pressure given through a booster pump.
|
| Output pressure 100 to 1200psi |
Output pressure 100 to 10,000psi
|
Application of piston pump
its main applications for different processes are as
- Varnishes and glazes
- Dispersion paints
- Water-proofing of buildings
- Bitumen and bitumen-like coating materials
- Fabric adhesives
- Sealants
- Plasters (filled)
- Latex paints
- Flame retardants
- Thick coating materials
- Zinc powder paints
- Iron mica paints
- Airless spraying fillers
- Corrosion protection
Advantages of a piston pump
- It has better pressure handling features than other types.
- Its high efficiency makes it more cost-effective than Pitot tube pumps.
- Its positive-displacement features make fluid flow directly related to speed and are used for injection applications.
- It also has high suction features for viscous liquids.
- Small designs operated with motors are preferred for pressure-producing features.
Disadvantages
- Its pulsating flow makes it ineffective for some applications needing a pulsation dampener.
- The piston pump initial cost is larger and makes the process costly. It is also used for cleaning liquids.
- Its components are high-cost due to the compact design and high accuracy.
- Maintenance is difficult and needed for working things like the pressure regulating valve, pulsation damper, and relief valve.
- Its size is larger, covering a larger area normally for V-belts. are larger in size since they have a motor on the pump head