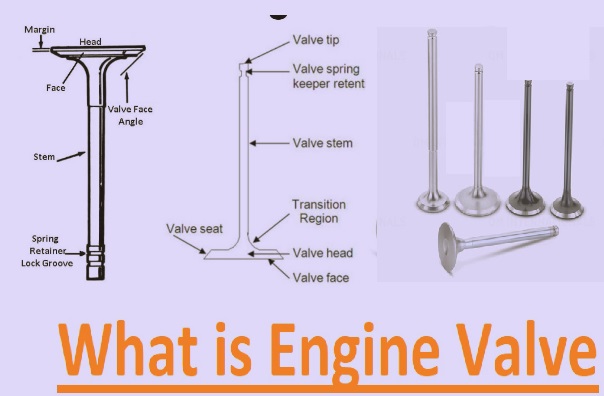
The engine valve’s main components work to control the internal combustion engine. It is basically a mechanical gate that controls air flow into the cylinder and releases exhaust gases when the engine cycle is performed in an internal combustion engine for maintaining power and efficiency. In this post, we will cover the detailed features of the engine valve. So let’s get started.
What is an engine valve?
- The engine valve is a mechanical part that is employed in an internal combustion engine for controlling fluid or gas flow in combustion chambers when the engine operates.
- It controls engine air intake and fuel-air mixture. When the vehicle moves, this valve regulates engine power output and air intake.
- A fuel-air mixture is added in the engine cylinder through the intake valve opening, and when the exhaust valve opens, fuel-air combustion burns and exhaust gases are produced.
- The burning process occurs, and the cylinder works well during the closing of both valves.
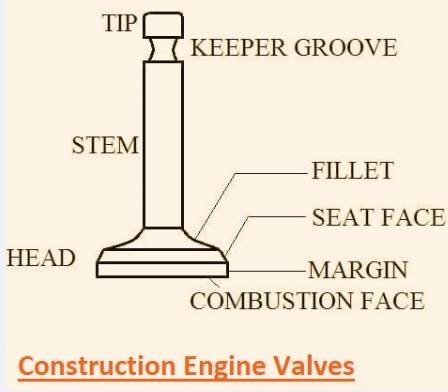
Engine Valve Structure
- Engine valve designs like poppet configurations provide up-and-down popping movement and come with a conical-profile valve head configured to a machined valve that seals the fluid path.
- Its certain design of valve head makes these valves mushroom valve designs.
- Its two main components are the valve stem and the valve head. The pinnacle comes with a fillet that causes the seat face to be configured at a certain angle to fulfill the machining of the valve seat.
- Valve face seating to the valve seat provides a seal to the valve against combustion pressure.
- valve stem configured with a valve at mechanical components of the engine that control valve by producing a force that moves the stem opposite to the seating pressures generated through the valve spring.
Types of Engine Valves
Types of engine valves based on working process and commonly used types are mentioned here.
Monometallic engine valves
- are made with materials that are combinedly employed to make the valve stem and valve head.
- This engine valve provides high resistance for heat and also friction resistance.
Bimetallic engine valves
- A bimetallic engine valve, also known as a bimetallic engine valve, is configured through 2 different material connections with friction welding techniques that make valves with a steel valve head and a valve stem of martensitic steel.
- Each steel provides certain features, while the steel of the valve head has high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, and the valve stem steel has high abrasive wear resistance and lasts longer.
Hollow engine valves
- The hollow engine valve comes with a bimetallic valve comes with a hollow cavity stuffed with sodium. With increasing valve temperature, sodium becomes liquid, and through movement of the valve, it circulates, dissipating heat through the warm valve head.
- The hollow design provides high heat transfer in the stem compared to a solid valve since martensitic stem materials are good conductors of heat compared to austenitic head material.
- Hollow valve is used in modern engines to provide high power with a small, high-density structure, with a high exhaust gas temperature that is not handled in a solid valve
Engine Valve Working
- Engine valve work through pear-like lobes that are cam-rotating on a shaft. The camshaft is operated through a chain, belt, and a set of gears on the crankshaft.
- camshaft configured over engine block having small metallic cylinder tappets in channels over cam and a longer metallic pushrod to the cylinder head.
- The upper part of the pushrod, according to the rocker arm that is against the valve stem, is held in position through a high-strength coiled valve spring.
- When the pushrod moves above the pivot, the rocker arm moves the valve downward opposite the spring pressure.
- When the cam lobe moves, the valve spring works to close the valve; this is called the overhead valve (OHV) system.
- Some engines are without pushrods, and other operating valves are controlled through single or double camshafts in the cylinder head.
- Overhead cam techniques are best and cause high power according to engine ability, compared to engines having pushrods, since they work with high speeds!
Symptoms of a faulty Engine Valve
Power Losses
- A faulty valve causes less engine performance and power losses. Valves fitted accurately, having less or no wiggle area. If oil is found leaking, a gap is generated, and heat is lost.
- A burnt valve also causes power losses and affects the engine’s working
Noises
- An engine valve is also bad if facing ticking sounds in the engine. When the vehicle is driven, ticking noises are highly produced.
- It occurs due to damaged valves affecting engine lubrication, which causes ticking sounds.
Smoke is released from the exhaust pipe.
- Blue smoke released from the tailpipe is a sign of a faulty engine. An engine valve causes blue smoke. Oil goes to the combustion chamber through the affected engine valve sealing.
- It causes oil and gasoline to burn. As a result, the driver faces oil level reductions.
Reasons of Engine Valve Problem
The main causes of engine valve faults are
- improper connections of valve springs and faulty valve clearance settings.
- It has bad hydraulic tappet connections and damaged components.
- Valve Misalignment and High Valve Guide Clearance
Engine Valve Mechanisms
Valves operated with cams connected to the camshaft. The camshaft moves through the crankshaft. When the camshaft rotates, the cam causes the operation of the valve.
Based on valve locations, two valve mechanisms used a straight poppet valve and an overhead poppet valve.
Valve-Tappet Clearance
- Clearance is added between the valve and valve stem for a straight poppet valve and for the rocker arm and valve for an overhead poppet valve.
- It is called valve tappet clearance, and another name is valve lash. Clearance manages valve stem expansion when the engine has a high temperature.
- If enough clearance does not exist, the valve will not adjust accurately during engine heating, which causes power losses and valve lifting.
- valve tappet clearance based on valve stem length, materials of valve, and engine operating temperature
Eccentric Rocker Arm
- Eccentric rocker arms manage differences in valve-tappet clearance. It has conventional rockets configured for holding eccentrically with a slot and pin. The
- • The plunger and spring regulate the eccentric piston. plunger operated through spring and oil pressures through the orifice of the rocker arm.
- During engine valve closing, the eccentric below the spring action and plunger moves for clearance.
- When the cam moves to open the valve, the plunger and spring reduce the shock through this motion. The valve becomes open when the cam is upside.
Valve Cooling
- The exhaust valve is running at a higher temperature compared to the inlet valve since the exhaust valve is making a connection with high gases, and the inlet valve is at a low temperature through the fresh charge. The exhaust valve becomes highly heated during short operations.
- The valve face experiences high temperature, and the valve stem is a cool component.
- The valve step delivers heat to the valve guide and valve faces, flowing heat to the valve seat and maintaining a cool valve temperature.
- For proper cooling, cylinder head designs should ensure proper water circulation over different parts of the valve.
- If the valve is accurately fitted on the valve seat and closes the combustion chamber, and no power and compression losses occur
- With that accuracy, proper valve seating makes connections with the valve seat where high heat transmission occurs.
FAQs
What is the valve of an engine?
- Engine valve: the main part that regulates the flow of air and fuel mixture into the combustion chamber and releases exhaust gases. It comes with two types of intake valves and exhaust valves.
What are the outcomes of an engine valve going bad?
- The signs of valve errors are noise, power losses, difficult ignition, fuel usage, and smoke releases from the exhaust.
- Engine valve replacement and removal are difficult tasks to perform. The main inspection of the valve seal is important for cleaning the combustion
How much does it cost to repair engine valves?
- Normal full replacement of a valve is 800 to 2200 dollars, based on conditions. A single valve replacement costs about 150 to 200 dollars. Valve replacement is costly due to labor expenses.
What happens when a valve is damaged in an engine?
- If a valve damages its components, they mix into the combustion chamber and affect the upper part of the piston and also the cylinder head.
What are the signs of a faulty engine valve?
- The main signs are ticking sounds, power losses, difficult ignition, fuel usage, and smoke releases in the exhaust.