Welding is the main process used to connect laser-cutting components and parts to make a complete design. Different types of welding methods are used, such as MIG and TIG welding, which use inert gases for the connection of metallic parts. Both come with features and work, each used for different applications. In this post we will cover details for MIG welding and TIG welding methods and find their differences. So let’s get started.
What is Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding?
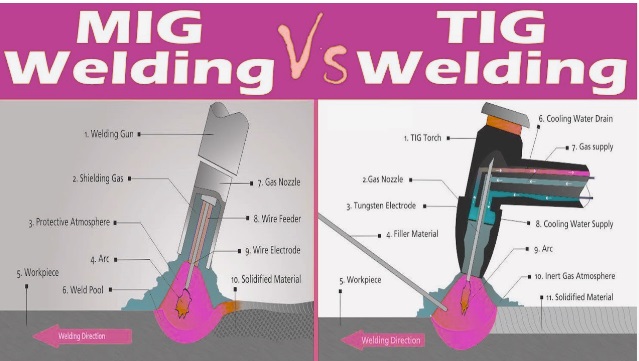
- MIG stands for Metal Inert Gas Welding, that is, arc welding that operates with a continuous connection between a solid wire electrode that gets melted over the tip and pushes molten metal from the welding gun at a high temperature.
- As a result, metal parts join and make a welding junction. A welding shield that is gas that protects the weld from any contamination particles.
- In this wedding method, a semi-automatic arc is used for producing a weld with wire electrodes for filler materials and shielding gas for protection of the weld.
- They provide easy weld penetration and minimize the effect of porosity in welding.
- Electrode and shielding gas added in welding gun. The shielding gas comes with a mixture of 75 percent argon and 25 percent CO₂..
- In 1949, MIG welding was patented in the US, but at that time, helium gas was used for protection arc and melting bath through a bare wire electrode.
What is Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding?
- TIG stands for tungsten inert gas, which is also known as gas tungsten arc welding. It also uses arc, but its electrodes are non-consumable tungsten electrodes that are used with distinct consumable filler material.
- Filler is like a rod that is put in the weld pool, so it is used in a manual process with hands for tungsten electrode and filler rod feeding.
- Each filler rod’s size and composition is based on weld creation. TIG welding uses shielding gas that is 100 percent argon, and CO₂ is used for MIG.
- • The TIG welding process uses a foot pedal that helps the welder control the amperage, set the heat at the time of welding, and provide accurate control for the heat added into metals.
Differences between MIG and TIG Welding
Power Supply
MIG Welding
- MIG welding is operated with a DC current power supply since it produces less weld spatter or faults in the well. DC is preferred for thin materials and provides a controlled welding process.
TIG Welding
- TIG performed with both AC and DC current sources. That helps welders to choose a power supply based on the material used.
Metal types
MIG
- MIG is good to use for welding and laser cutting of mild steel and cast iron. MIG welding does not generate aesthetic welds, but metals are easy to work with, and the controlled process makes the weld connection clean and smooth.
TIG
- TIG is good to use for aluminum laser-cut welding and stainless steel. TIG welding is highly accurate as compared to MIG welding; that is good for metals that need careful handling.
Electrode
Read also:Why is Underwater Welding So Dangerous?
MIG Welding Electrode
- MIG welding electrodes are consumable; they are put in the torch and melt and connect with the metal through the current. The electrode connects with welded metal and reinforces the welds.
TIG Welding Electrode
- TIG electrodes are made with tungsten and are non-consumable. The tungsten rod provides current, and the distinct filler rod melds to welds.
Shield gas
MIG Welding
- The commonly used gas mixture for MIG welding is argon and carbon dioxide. That mixture is good to use for thick metals, but the gases used are lightweight and easily carried off and are dangerous for welding. Flux core welding is MIG welding that does not use a shield gas supply.
TIG Welding
- TIG welding uses argon and nitrogen or sometimes pure argon. The shield gas part of TIG welding prevents the electrode from overheating and getting too heavy as compared to oxygen that protects the weld from splatter.
Welding quality
MIG Welding
- MIG welding is durable and high strength and good to use for high load conditions. But it is difficult to make accurate welds with the use of MIG welding but provides durability features.
TIG Welding
- Small beads are easy to make with accurate features and good welds with the use of the TIG welding process. TIG welding is high strength and good to use on thin metals.
Speed
MIG Welding
- • A welding torch helps to feed filler rod automatically. MIG welding is high speed as compared to TIG welding. MIG welding is best to use for bulk production since it has high speed.
TIG Welding
- In this welding, a filler rod is added to the welder manually. TIG welding is slower than MIG welding. The tungsten electrode of TIG welders overheated quickly if air-cooled.
Cost
MIG Welding
- MIG welding is a low-cost method compared to the TIG welding process. Since less preparation is needed for MIG welding, it is a higher-speed process than TIG welding and easy to afford.
TIG Welding Cost
- • The TIG welding process is high cost, but the slow speed makes it a costly process, but it is a precise process.
MIG vs TIG vs Flux Core
| Type | Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding |
Flux Core Arc Welding (FCAW)
|
| Welding Speed | Fast | Slow | Fast |
| Skill Level Required | Beginner to Intermediate | Intermediate to Advanced |
Beginner to Intermediate
|
| Filler Material | Consumable Wire Electrode | Filler Rod |
Consumable Flux Core Wire
|
| Shielding Gas | (CO2, CO2/Argon Mix) | (Argon or Helium) |
No
|
| Welding Applications | General Purpose | Precision and Critical |
Construction and Heavy-Duty
|
| Portability | Moderate | High | High |
| Equipment Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
| Welding Positions | All positions | All positions |
All positions
|
| Weld Bead | Thin to Thick | Thin to Thick |
Medium to Thick
|
| Weld Appearance | Good | Excellent |
Average to Good
|
| Heat Input | High | Low | High |
Advantages of MIG Welding
- MIG welding is a high-speed process that takes less time for setup preparation. It provides clean outcomes in a small amount of time.
- MIG welding is an easy-to-afford process. It needed some consumables, and they are low-cost options.
- It is a highly accurate process with less effort since you just manipulate the torch for the welding process.
- Filler rod is mechanically added through the torch. MIG welding is a semi-automatic process that makes a clean bead with small splatter.
- MIG welding uses different metals and is also used for different applications.
Disadvantages of MIG Welding
- It uses a DC power supply, and the arc through the electrode has low stability and causes error in the weld.
- MIG welding generated high ozone and nitrogen oxides at the time of the welding process.
- If not accurately cleaned, metal gets corroded after the welding process as oxide layers do not seal the weld completely.
- Easily cut through metals with these welding methods if not moving the torch accurately. So it is used for thick metals.
Advantages of TIG Welding
- TIG welding is a more accurate process than MIG welding since it operates through manual control.
- TIG welds come with easy cleaning features and are smoother and more pleasing than MIG.
- It has a low effect on environments since it uses argon gas, which is less hazardous.
- It provides good control features since the separate filler rod and torch help to provide manual control.
- MIG welders use continuous buying and replacement of electrodes in torches, and TIG welders use separate filler rods.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
- TIG welding materials and units are high cost and time-consuming. It is a high-cost process.
- Parent metals need to be accurately cleaned and ground to provide welds with a clean surface for welding.
- TIG welding needs experts to perform since they properly hold both the filler rod and the torch.
- MIG welding helps to breeze through the welding process, but accuracy is needed for TIG, which is a time-consuming process.
Conclusion
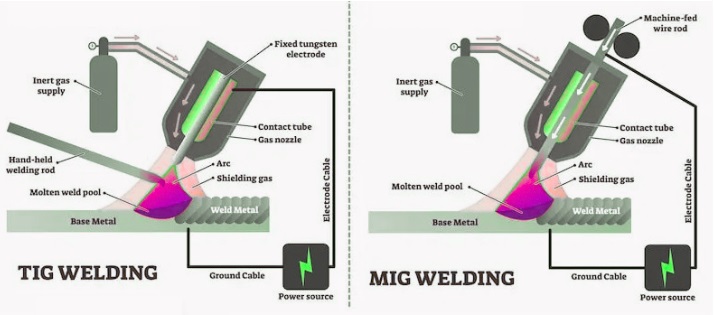
MIG welding operates with continuously fed electrode wire and shielding gas through a handheld torch. While TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode with shielding gas provided with a supply line and a handheld filler rod that is put into the weld pool.
TIG welding uses a torch-configured controlling process or foot pedal for varying amperes. These two welding processes use different shielding gases.
MIG welding is low cost, high speed, and easy to use. TIG welding is a difficult process and needs skilled welders and also is high cost. But TIG provides higher accuracy and quality than MIG welding.
Uses for TIG Welding
- TIG welding is used for thin materials and helps to make a clean weld without any burning of materials.
- It is good to use for aluminum and copper, which are nonferrous metals, in the TIG welding process.
- TIG welding is used in shops or in stable conditions.
- For small projects that need high accuracy, TIG is good to use.
FAQs
Which is better, TIG or MIG?
- It is not easy to define which is better, either TIG or MIG; that is based on different parameters. TIG is a high-strength weld and looks good with an accurate, skilled welder; for a low-skilled welder, MIG welding is a good option.
- MIG welding is a higher-speed process than TIG welding, providing a longer run in a short time.
Is TIG welding more difficult than MIG?
- TIG welding is more difficult than MIG welding since it is a low-automated process that needs high accuracy.
Should I learn MIG or TIG welding?
- MIG welding is better for beginners than TIG welding.