The lathe machine is a mechanical tool or device that is commonly used for heavy industry. It operated through a swarf removal process for cutting purposes, shaping of materials, and polishing of different parts made with different materials. There are different types of lathe machines, and each has its own function, such as milling, revolver, and automatic. These machines are also defined based on tabletop and benchtop lathes.
In this post we will cover details and features for different parts of the lathe machine. So let’s get started with
What is a Lathe Machine?
- The lathe machine is the main part of machining tools that is used for turning. It provides rotation for working components on an axis with static cutting tools to convert them into the required shape.
- This process helps to make objects through symmetrical design over an axis of rotation, like basic wood bowls and complicated designs.
- With the start of the Industrial Revolution, the lathe has become the main component of machining parts and tools.
- It is used for making molds of components made with different materials that are difficult to handle with high force and accuracy.
- The main uses of a lathe are cutting, threading, and parts finishing which provide a high level of production and provide smooth finishing for series manufacturing.
- The main uses of lathe machines are in the vehicle, computer, electrical, and woodworking industries, as well as part of threading, cutting, turning, boring, etc.
Working of Lathe Machine
There are different steps involved for working of lathe machines that are as
Preparation
- First of all, it is important for preparing the machine and working component. That comes with providing lathe machine accurate cleaning and other connected components like the lathe bed, tailstock, and headstock in accurate alignment.
- After that, the working component is configured on the lathe. That is placed between the middle of the headstock and the tailstock through connection with the chuck.
Selecting Cutting Tool:
- Select the cutting tools through using materials of the working component and required working. The tool is accurately fixed in a tool holder that provides proper position and accurate assembly for the working component.
Spindle Speed:
- The spindle speed is the main factor for the working of the lathe machine. So set it based on material types and for certain cutting functions. The spindle gets power from the motor for providing rotational motion for the working component.
Manage Feed:
- Engage feed after setting of spindle speed. The feed moves the cutting tool over the longitudinal direction of the lathe bed, which provides accurate cutting. This motion is manually controlled at a steady rate and performed with a lead screw and feed rod feature.
Cutting Operation:
- The cutting process started with making a tool connection with the rotating component. The lathe removes undesired parts from the working component, which rotates to make its required shape. Different working techniques, like turning, facing, grooving, and threading, are made with moving tools in different directions and depths on the component.
Adjusting:
- It is important for monitoring the cutting process and providing the required adjustment. That comes with the shaping and dimensions of the machining working component, so make the cutting tool in the proper shape and set the feed rate and spindle speed according to the requirement.
Final Inspection:
- After completing the machining function, the working component is inspected for high accuracy and final finishing. Some steps, like sanding or polishing, can be used for a lathe to get the required surface finishes.
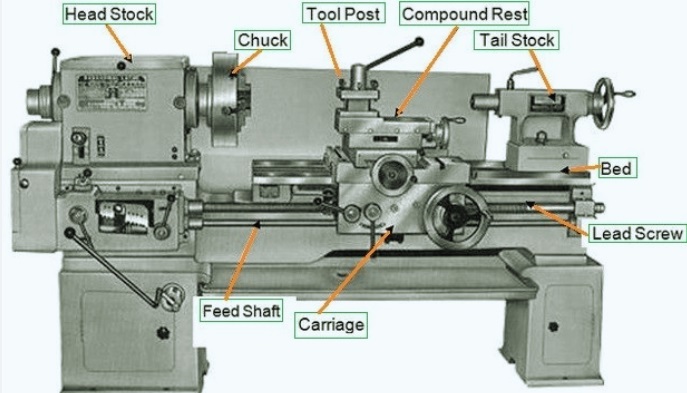
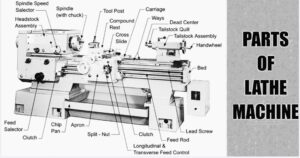
Different Parts of a Lathe Machine
Headstock
- The headstock is the main component of the lathe machine that is called the powerhouse. It lies on the left of the bed and comes with a spindle and motor that control working component rotation. The headstock is used for providing power and the required speed for machining functions.
- The headstock is used for holding and rotating the working component at different speeds, based on the materials and working needed. It is important for defining spindle speed that has an effect on the accuracy of the machining process.
- The spindle of the headstock gets power from the motor. When the motor operates, it provides power to the spindle; as a result, it rotates. Different parts like chucks, faceplates, or collets are configured on a spindle that firmly controls and holds the working component in position during working.
- For an accurate working headstock, there is a need for proper speed features, and make sure the spindle is accurately aligned. Material hardness and cutting type are needed to affect speed where the headstock operates.
Tailstock
- The tailstock exists opposite to the headstock, and this part is used for providing some support for the working component at the time of functions. It has moving features over the bed and handles working components at different lengths.
- The tailstock provides stability for the working component for longer machining operations. It is also configured with a drill chuck for boring functions.
- Tailstock moves over bed and locks in required position for handling working component. If the drill process required the quill extended for driving the drill bit in materials
- For working of the tailstock, there is a setting needed over the bed for alignment of the spindle. After that, the tailstock locks and gives support for stable rotation of the working component.
Bed
- This part of lathe work as a basesupported different parts of the machine, like the tailstock, carriage, and headstock as well.
- It provides proper alignment and accuracy through holding components at certain positions. The bed needed to be accurate, stable, and rigid for avoiding any motion at the time of working that would affect working accuracy.
Carriage
- The carriage is the main part of the lathe machine, used for holding and moving cutting tools. It moves over the bed that provides accurate cutting, drilling, and working component shaping.
- The carriage holds cutting tools and moves over the surface of the working component for providing proper machining function. Its main workings are turning, facing, and threading.
- The basic working of the carriage is to move longitudinally over through the handwheel or lead screw. The cross slide component of the carriage moves the cutting tool at 90 degrees to the working component. This type of motion helps to make different shapes of components and cut at different angles.
Lead Screw
- The feature of the screw is to align different threads through the bend. For smoothing other refinements with working components, a smooth screw gets the screw position.
- The lead screw is important for threading or for providing automatic feeding for longer cuts.
- The lead screw is regulated with the headstock and rotates through the spindle. that turns the carriage over the bed that provides threading and feeding with high accuracy.
- When you set required parameters, operators adjust the lead screw, and the carriage moves to cut threads with smooth accuracy over the working component.
Feed Rod
- Feed rod moves over lead screw and parallel with bed. It provides power to carriage motion for non-threading operations. This rod is important for constant motion of the carriage; at the time of turning, functions provide smooth cutting.
Spindle
- It lies in the headstock, and the spindle is rotated with the motor. This component holds and rotates the working component. The spindle is the main rotation part where components are connected, and its speed and rotation are regulated with different machining operations.
Chuck
- It is connected with a spindle that holds the working component in a certain position. Chuck can have 3 or 4 jaws that provide different shapes and sizes for working components to provide strong holding for the machining process.
Tool Post
- It lies on carriage parts and holds cutting tools. It helps the tool to be set at different angles, which provides flexible features for performing different cutting functions. The tool post is a variable component of a lathe that provides accurate control for cutting tools at the proper position and direction.
Cross Slide
- It is also configured on the carriage, and it moves at 90 degrees to the bed. This part provides motion towards the working component and away from the component that is important for depth control for cutting operations. It provides accurate setting of the position of cutting tools and, as a result, makes proper depth cutting.
Compound Rest
- This part of the lathe machine lies at the upper side of the cross slide and is used for angle cutting and accurate tool setting. It provides accurate cutting angles and finishing work that accurate angle cuts and performs complicated machining operations.
Apron
- The apron component of the lathe carries the control system. It comes with gears, clutches, and levers used for controlling the motion of the carriage and cross slide. It is important for controlling and setting the position of the carriage and motion at the time of machining functions.
Guideways
- For the tailstock and carriage to move accurately on the bed, it has guideways that lie internally and externally.
Tool Turret
- The turret on the lathe provides a sequence of operations for tools that changes with the completion of other parts. The turret comes in different sizes based on cutting tool dimensions and numbers.
- rotation of CNC lathe tools The turret is based on programming and commands given to CNC lathe machines.
Slide Box
- It is a box that comes with a control system for lathe feed motion. That comes with devices that convert the rotary motion of the light rod and lead screw into linear motions of the tool post.
Gearbox
- The gearbox for the headstock provides different speeds through accurate geometric ratios based on lever position.
Chip Pan
- At the low side of the lathe, the chip pan gets extra materials during machine working.
Handwheel
- This is a wheel that moves different components like the cross slide, tailstock, carriage, etc., and these components have handwheels for manual operations.
Cooling Device
- The basic working of a cooling device to control the temperature of the cutting part of working materials. A cooling water pump helps to remove slotted fluid in the reservoir and sprinkles it on the cutting part for washing chips.
- The proper cleaning of tools increases working life. The tool performs surface finishing work on working material.
Legs
- These parts of the machine provide support for holding the complete weight of the machine. Cast legs are commonly used. Both legs are bolted to the ground with the use of anchor bolts for controlling machine vibrations.
Common Operations of Lathe
The lathe machine is used for processing of different materials such as metal and wood. For processing, it rotates working materials on an axis, and a cutting tool is used for removing materials, shaping, and particle modification. The different processes performed at the lathe machine are as follows.
Turning:
- It is a basic process where a lathe removes materials at the external diameter of a working component for minimizing sizes and making a cylinder-like design. Turning makes a smooth surface and provides accurate diameters and dimensions.
Facing:
- In this process cutting tools move at 90 degrees to the axis of rotation of materials for making a flat surface at the material’s end. It is used for reducing working materials.
Drilling:
- A lathe machine is used for drilling operations; for this purpose, the tailstock holds the drill bit. The rotation of the working component is drilled to make holes over the length at certain points
Boring:
- Boring is the inner turning that increases or smooths the hole of working materials. It is used for providing accurate inner diameters of materials.
Threading:
Lathe machines cut threads on external and internal surfaces with coordination of spindle rotation through a lead screw. This process is used for making screw threads for bolts, nuts, and other threaded parts.
Knurling:
- This process helps to make different patterns for working components for the grips process. It is performed with the use of different tools and materials when it rotates.
Grooving:
- This process provides cutting for narrow channels on working components for seal rings and other components accuracy.
Parting:
- This process cut the working component for separating into two parts. The parting tools are put into rotating materials to a central point and then separate.