Welding porosity is a fault in welding that results from gas bubbles trapped in the welding metal at the time of solidification. Welding porosity affects welding in different ways, like look and strength, reduces resistance to corrosion, and also causes weld failure. The importance of porosity in welding and its solution for solving this fault are also important. Let’s get started with “What is Porosity in Welding?
What is welding porosity?
- Weld porosity is a welding fault that results from different gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen being absorbed and trapped in the molten weld puddle and changes in weld solidification that make pores on the surface of the bead. Porosity exists on the surface of the weld and in the weld bead.
- Improper gas shielding is a cause for the absorption of gases in the weld pool. Porosity occurs in different directions and uneven distances, but normally we can see it one inch from all sides.
- Porosity reduces the working cross-sectional area of the weld, which also affects tensile strength, impact toughness, and fatigue strength.
- There is a premature fracture that occurs as a result of stress concentration and the crack initiation site due to porosity.
Causes of Porosity in Welds
Welding porosity due to gas trapped in the molten weld pool. There are different reasons for gases from different sources that are.
Base Metal Contamination
- Dust, oil grease, rust, moisture, and other materials added gases in the weld pool with the shielding gas. These contaminants also react with the weld metal and make oxides that cause porosity.
Improper shielding flux
- Shielding gas is employed for the protection of the weld pool due to atmospheric contamination and oxidation. If shielding gas is not good to use for the welding process, that results in porosity. Such as the use of shielding gas with high-level oxygen, which causes weld metals to release carbon dioxide bubbles. The use of flux with high moisture causes hydrogen cracking in weld metal.
Faulty welding technique
- Welding methods also affect heat input, penetration, arc stability, and deposition rate of weld metal. If this process is not handled carefully for the welding process, that is the cause of porosity. Like if we use high or low current, that also causes spatter. If you use a longer or shorter arc length, that causes arc blow.
Poor electrode storage
- The electrode is a source of filler metals and, in some conditions, shielding gas for the weld pool. So electrode conditions affect weld metal quality and result in porosity. Such the use of a contaminated electrode added moisture into the weld pool. The use of faulty electrode size results from mismatched features and composition of weld metal.
Read also:Why is Underwater Welding So Dangerous?
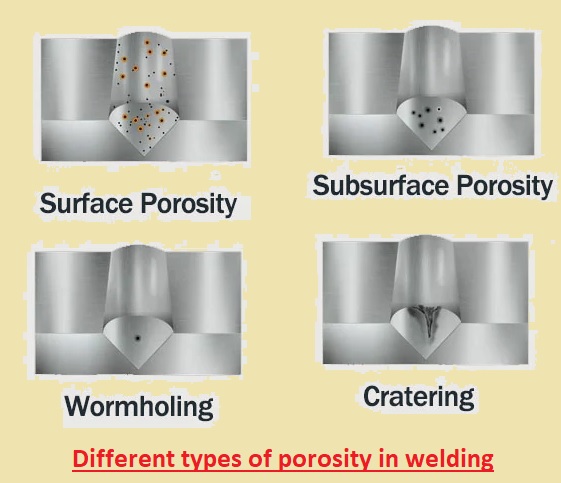
Different types of porosity
Surface Porosity
- It is a common type of porosity that is also called surface-breaking pores. This porosity type looks like Swiss cheese when seen with the naked eye. Pores are on top of the bead, smoothly spread on the bead.
Subsurface Porosity
- This type of porosity is hidden below the bead surface. This porosity is difficult to detect. An X-ray or grinder is the best tool for the detection of this type of porosity. This type of porosity is also shown with small bubbles that expand like bead cooling.
Wormholing
- Wormhole porosity is shown if slag is removed from the bead through the use of flux. Wormholes are elongated pores that are like worms burrowing over the top of the bead or down the bead.
Cratering
- Catering is a small divot that is normally seen at the end of the bead. Cratering is a process that is a result of gravity and shrinkage of molten metal at the time of solidification.
Effects of Porosity in Welding
Welding porosity comes with negative factors on weld quality and working features.
- The existence of gas bubbles in weld metal minimizes the cross-sectional area and creates stress concentration points. It reduces tensile strength and ductility and causes cracking in high load conditions.
- Gas bubbles in weld metal make pits that trap moisture. That increases corrosion, and it increases with time.
- Gas bubbles in weld metal also affect its look and make it rough. It also has a bad effect on aesthetic value. A gas bubble in weld metal has a bad effect on inspection and testing.
How to avoid porosity in welding?
Follow these points for preventing porosity in welding.
- Properly cleaning base metal and filler metal before welding helps to remove contamination that makes gas bubbles in the weld pool. With the use of a wire brush, solvent removes oil, grease, paint, rust, and moisture from welding surfaces.
- Use a proper gas mixture that is according to the base metal and filler metallic composition, and provide protection from any contamination. To avoid any leaks or blockages, check the gas flow rate and pressure. Do not weld in draft conditions that can affect shielding gas coverage.
- Set the welding process to avoid extra spatter and incomplete fusion. Use accurate arc length, travel speed, and electrode angle to provide a smooth weld pool. Do not do extra weaving that traps gases in the weld pool.
- Define welding machine parameters based on the recommendations of manufacturers and the welding process. Apply accurate voltage, current, polarity, and wire feed speed for base metal and type. Apply accurate transfer mode for filler metal and shielding gas, like short circuit, spray, or pulsed transfer.
How to fix porosity?
- Either you follow all precautions, or there is a chance of the existence of porosity. To fix it, follow these points.
- The basic method for preparing weld porosity is the removal of the porous part of the weld to the base materials. Try to weld on the affected bead to make porosity.
- The thin grinding wheel is a good tool for solving this operation. The entirety of porosity was removed with small base metal reduction.
- After removing the affected part, it needed to be cleaned to avoid any contaminants adding into joints.
How much porosity is acceptable in a weld?
- There is no straightforward answer for this question that is based on welding construction code. The American Welding Society follows these points.
- That says the diameter of porosity is about 3/8 inches (or 9.4mm) or less in linear inches of weld and 3.4 inches for a12-inch length of the weld.
FAQs
What are the reasons for porosity in welding?
- The main causes for contamination of base metals are atmosphere sneaking in the weld pool due to faulty shielding gas, mechanical errors such as cracked MIG liners, worn O-rings, or bad welding methods.
Is it possible to weld over porosity?
- No, first remove the fault by completely removing the porous part of the weld towards the base materials and cleaning before welding that part.
Is it possible to burn porosity out of a weld?
- It is possible to burn porosity through tuning amperes more than 310 and welding back to bad welds. That can cause different types of issues based on the work.
How to remove porosity?
- Commonly used methods for removing porosity are ultrasonic mixing, cement pressurization, and vacuum mixing. These methods cause porosity reduction from 8 percent, which is what you get with hand mixing, to a value less than 1 percent with vacuum mixing.
What are the repairing processes of porosity?
- The main method for preparing weld porosity is to remove the porous part of the weld toward the base materials.
How to avoid porosity?
- To avoid weld porosity, it is good to use accurate welding methods and use materials and installations for welding in good conditions. That is accurate cleaning and base materials preparation and the use of accurate welding wire. Set enough shielding gas coverage.
What are the errors of porosity?
- Porosity resulted in hole creation in the weld pool, which resulted from gas bubbles that were trapped. It is a common welding fault when using shielding gas, which exists in welding methods like stick welding.
What welding method causes porosity to form?
-
- It is the result of gases that are trapped in molten metal at the end of the welding process. Porosity causes different welding types such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding.