A septic system is an underground wastewater treatment system that is normally seen in rural areas where a centralized sewer system does not exist. It comes with a septic tank that digests organic materials and separates floatable materials like oil and solid waste existing in wastewater.
In this system, nature and the latest methods are used for wastewater treatment that is produced in your kitchen, laundry, and bathrooms.
The main components of septic systems are the septic tank and soil absorption field. In this post, we will cover detailed features for this system and its working.
Septic Systems Working
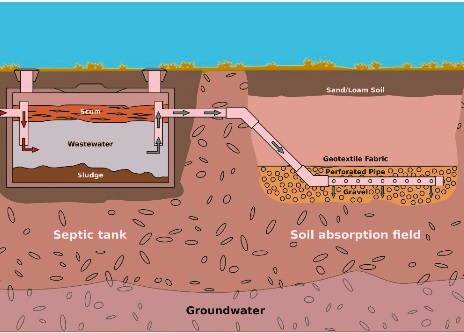
- The basic septic system comes with a septic tank and a drain field. The septic tank works to digest organic materials and removes oil and other floatable materials and solids existing in wastewater.
- In the conventional method, liquid is discharged from the septic tank in perforated pipes connected to leach fields, chambers, and some other structures for releasing effluent into the soil, which part is called the drainfield.
- Some other system uses pumps for septic tank effluent to trickle through sand and other particles to eliminate pollutants such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and other particles.
Conventional septic system working
- The working is that water moves out of the house through one drainage pipe and goes to the septic tank.
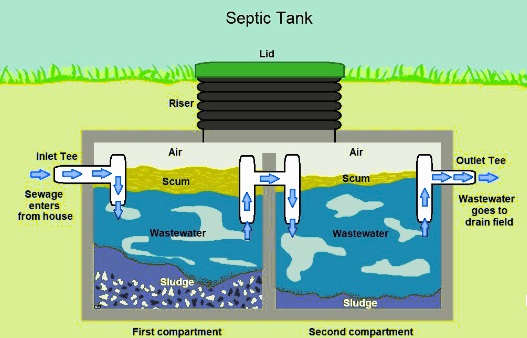
- The septic tank is located underground and made of concrete or fiberglass and used for the creation of a watertight container. Its working is to control wastewater by helping solids to settle to the lower part, forming sludge, and oil and greases float at the upper part in the form of scum. T-shaped outlet: avoid scum leaving the tank and moving into the drainfield area.
- The wastewater leaves the tank and goes to the drain field. That is shallow, covered, and made in unsaturated soil. Pretreated wastewater is removed through piping on porous surfaces that help wastewater to move through the soil. Soil gets and disperses wastewater since it percolates in soil and discharges to the underground.
- If the drainfield has a high volume of liquid, it can move, and as a result, sewage can flow to the ground surface or also move towards tile backups.
- In the last, wastewater percolates in soil, removing harmful coliform bacteria and nutrients.
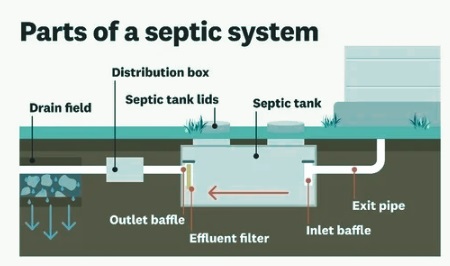
Parts of a Septic System
There are two components of a septic system. The first one is the septic tank, and the second one is the absorption field.
Septic Tank
- The septic tank is the main component, and the complete working of the septic system is based on this tank. It is the first part of treatment for wastewater when it leaves the house.
- The design of internal plumbing is such that hoses feed directly into the septic tank externally at home.
- The septic tank works to hold wastewater for a certain time that helps the decomposition of microorganisms in household waste and treats wastewater before removing it from the tank. It is done through separation of waste materials into three different layers.
- • The first one is a scum layer existing on top where fats, oils, and greases exist that is less dense as compared to water. On the lower side of this layer, microorganisms exist to treat and break down wastewater in the septic tank.
- The 2nd layer is a clear layer that comes with the main liquid. That liquid is important for microorganisms to exist and work in septic systems. When microorganisms break down suspended solids existing in that layer, they move to the lower side and mix in the third layer, which is sludge.
- • The 3rd layer is sludge layers that come with solid waste, and anything that moves towards the septic tank is highly dense as compared to water. This continuously grows with regular use of the septic system, and the main method is to remove it through the use of a licensed septic disposal contractor.
-
- In the above figure, you can see that there are many parts of the septic tank that help to continuously use the system without any problems.
- • The first part is inlet and outlet tees that are coming from pipes in and out of the tank to below scum layers in the water. That move was to tee up through hydraulic pressure and out the absorption field when water moved in the house.
- Tees help the scum layer to be on top in the septic tank with sludge layers so no solids move to the absorption field.
- Without solids can clog and minimize the efficiency of theabsorption field.
- Septic tanks also come with risers and lids. New types of septic tanks come with risers and lids at grade for maintenance, pumping, and inspection.
-
Size of Septic Tank
- The size and dimension of septic tank size are based on the number of bedrooms in your home. Size is defined to know how much water flows in the system on a daily basis. If you have a large-sized tank, it will be high cost. Here we have made a rough idea based on your bedrooms that helps to make the size of the septic tank.
Two Bedrooms:
- If you have a 2-bedroom house that needs septic, it will have a750-gallon septic tank. In some municipalities, a 1000-gallon tank is the minimum size.
Three Bedrooms:
- The 3-bedroom house will use about a 1000-gallon water tank that handles about 360 gallons in a single day.
Four Bedrooms:
- The 4-bedroom home uses a larger tank size that has a volume of about 1250 gallons, and it can handle about 480 to 600 gallons in one day.
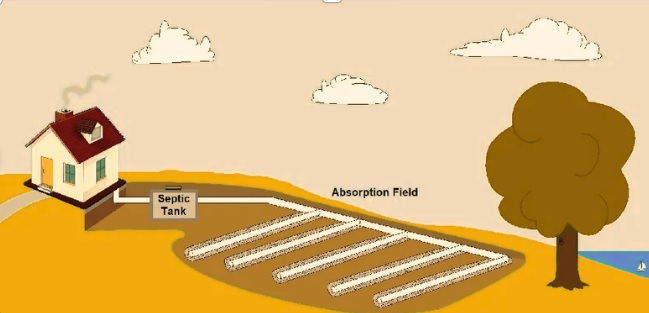
Absorption Field
- When wastewater leaves the septic tank, it moves to the absorption field. It is part of a system where water is absorbed through soil and grass.
- At a basic level, an absorption field comes with pipes in series having holes in gravel trenches that help water leak into pipes and underground soil. Water was treated with filtration into soil and absorption through grass.
Absorption fields are simple design like pipes connected in gravel trenches. The soil on certain places shows a type of absorption field used for wastewater for disposed of underground in effective way.
Septic System Diagram
The main diagram of septic system can seen here.
Septic Tank System Cost
| Type | Cost |
| Anaerobic | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Aerobic |
$10,000 – $20,000
|
| Gravity | $1,500 – $4,000 |
| Mound |
$10,000 – $20,000
|
| Chamber | $1,500 – $5,000 |
| Conventional | $2,000 – $5,000 |
Signs of a Bad Septic System
Here are some symptoms of septic systems shown.
- Water and sewage from toilets, drains, and sinks are leaking in the home.
- Sinks, bathtubs, and showers are draining slowly.
- Plumbing system has gurgling sounds, and standing water is seen close to the septic tank.
- There is a bad smell seen around the septic tank.
- Algal blooms are also seen in ponds and lakes.
Types of Septic Systems
Septic Tank
- The septic tank is an underground and watertight tank made for getting and treating wastewater at a partial level. It settles solids to the bottoms of tanks, and greases and light solids float. Solids stay in the tank, and wastewater is removed to the drainfield, where further treatment is performed.
Conventional System
- The conventional decentralized wastewater treatment system has a septic tank and a trench called a drainfield. The conventional septic system is connected to a single-family home.
- The gravel drainfield is made to work for many years. The effluent is piped from the septic tank to a shallow underground trench of stone.
- The geofabric is put on top of the trench to avoid different contaminants from entering into the clean stone.
- Effluent filters through stone and then is further treated with microbes when it reaches the soil existing below gravel.
- Gravel system is larger in size in design and not good to use for residential sites.
Chamber System
- Drain fields without gravel have been used for more than 30 years in different areas, and it is a conventional method used for gravel systems. It comes in different types, such as open-bottom chambers, wrapped pipes, and synthetic materials like expanded polystyrene.
- The gravel-less system is made with recycled materials and has a low-cost carbon footprint.
- The main example of a gravel-less system is a chamber system. That is used as a replacement for a gravel system. The main benefit is that it has an easy-to-make design and is easily delivered.
- It is good to use for high groundwater tables, and used for influent volume for septic systems that are not constant, also in areas where graves are rare.
- It also comes with connected chambers in series combination. There is soil-filled area around the chambers.
- Pipes carry wastewater from the septic tank to the chamber. The installation cost of this system is about $2000 to $5000.
Drip Distribution System
- The drip distribution system is effluent dispersion that employs different drainfields. The main feature is that it does not use a larger mound of soil since drip laterals are put into 6 to 12 inches of soil.
- The main disadvantage is that it uses a larger dose tank after the septic tank for handling proper dose delivery of wastewater for drip absorption.
- It also uses power, which makes it a costly system and increases maintenance.
Aerobic Treatment Unit
- Aerobic treatment units come with different processes for municipal sewage plants, but they work for smaller areas.
- The aerobic system added oxygen into the treatment tank. The more oxygen, the better the natural bacterial activity in the system, which further gives more treatment for nutrients in the effluent.
- Some aerobic systems come with a pretreatment tank, and the final treatment tank comes with disinfection for reducing pathogen levels.
Read also: What Is E-clip? Features, Working, Removing Process
FAQs
What are the 3 types of septic systems?
- Standard Septic System.
- Low-Pressure Dose System.
- Supplemental Treatment System.
What is the cheapest type of septic system?
- The anaerobic septic system is commonly used in homes and is a low-cost option.
What is the difference between a Type 1 and a Type 2 septic system?
- The basic difference between type 1 and type 2 septic systems is that type 2 septic systems come with an extra secondary wastewater treatment stage.
What is the most expensive type of septic system?
- Aerobic systems are high cost for installation, which is about $8000. The anaerobic system is low cost and has a value of about $4000 for installation. A conventional system is a common and low-cost septic system that costs about $2000 to install.