For diagnosing the vehicles, the DTC code is an important tool. Those called diagnostic trouble codes are an important factor in the indication of the vehicle faults. This code is produced through the diagnostic system and gives details on the health and working of the vehicle. In this post, we will cover details for DTC codes and related factors. So let’s get started
What Are DTC Codes?
- DTC codes are given by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The main use of these codes is as a vehicle’s self-diagnostic system.
- Codes come with alphanumeric characters and are shown on the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD) when any error is found in the vehicle.
- DTC gives details about errors in vehicles and locations where faults exist.
- Since codes give data about the vehicle, they are so important for vehicle users and technicians.
- If a high fault exists, the check engine light comes on; that is an indication of DTC.
Read also:What are Different Types of Bolt Heads
DTC CODE TYPES
DTC comes in two main types.
Generic:
- Generic codes are standard for all vehicle models and are applied universally.
OBD-II:
- It is used for lightweight and medium-duty vehicles that weigh in the range of 6,000 to 26,000 lbs.
J1939:
- It is used for heavy-duty vehicles such as transit buses and cement trucks.
Manufacturer-specific:
- manufacturers’ specific codes used for certain brands or models.
- These codes give more details of the vehicle system.
- OBD SCANNERS are used for DTC CODE decoding. After decoding, codes are interpreted through use of the code reader manual with the online database.
DTC codes are considered an important tool for vehicle diagnostics that give details for vehicle working conditions.
Through getting a proper understanding of these codes, we can find errors and solve them instantly.
Where do DTCs originate?
- DTC code is generated through the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system if faults exist in the vehicle. The OBD diagnostic system diagnoses faults and shows DTC as an indication of faults, and the check engine light gets on.
- We can also use an OBD scanner for decoding, dtc through the vehicle’s onboard computer system.
- Two main standards for DTC are OBD-II and J1939.
- Using OBD-II DTC in standard form comes with codes for all manufacturers that are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
Read also How To Remove Skunk Smell From Car
Types of DTC Codes
Critical Codes
- Critical codes show instant or urgent DTC codes that can badly damage the vehicle.
- Such a high engine temperature or low coolant level means the engine is not working well.
- Assessing these codes through real-time Vehicle diagnostics helps users to find serious errors and give instructions and solutions for the errors. This code helps to avoid any serious errors.
Non-Critical Codes
- Such codes are not high-intensity faults and do not need instant action. But they are important for solving errors at a time before they become serious faults.
- Non-critical codes are an indication of emission based on engine faults and high pollution. Normally, non-critical codes come with the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), which is the Check Engine Light.
How to Interpret DTCs
First character
OBD-II codes, first of all, have letters that show vehicle parts that are
- P: Powertrain, which comes with transmission, engine, and other connected parts.
- C – Chassis. it comes with a mechanical system, steering, suspension, and a braking system.
- B – Body. in this system, the parts involved exist in the passenger area.
- U – Network & vehicle integration. function controlled with an onboard computer system.
Second character
- • The second letter comes with zero or one.
- 0 – Standardized (SAE) code, called generic code
- 1 – Manufacturer-specific code
Third character
For powertrain codes, these codes explain which system is facing faults like
- 0 – Fuel and air metering with auxiliary emission controls
- 1 – Fuel and air metering
- 2 – Fuel and air metering, injector circuit
- 3 – Ignition systems or misfires
- 4 – Auxiliary emission controls
- 5 – Vehicle speed control, idle control systems, and auxiliary inputs
- 6 – Computer and output circuit
- 7 – Transmission
Fourth and fifth characters
- Last are numbers that show accurate errors that the vehicle has. It shows in numbers from zero to 99.
Common code examples are
P0782 shows powertrain, transmission, generic, and 2-3 shift malfunction.
COMMON DTC Codes Directory
- P0101: A Mass Air Flow (MAF) circuit
- P0110: Intake air temperature sensor circuit faults
- P0442: A small system leak within the vehicle’s evaporative emission control system
- P0500: A malfunction in the vehicle’s speed sensor
- P0606: A PCM powertrain malfunction
- P0706: A transmission range sensor circuit range fault
some other areas
| Code | Description |
| P0101 |
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor or circuit fault
|
| P0110 |
Intake air temperature sensor circuit malfunction
|
| P0120 |
Throttle pedal position sensor or switch A circuit malfunction
|
| P0130 |
O2 sensor circuit malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
|
| P0141 |
O2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
|
| P0215 |
Engine shutoff solenoid malfunction
|
| P0300 |
Random or multiple cylinder misfire detected
|
| P0352 |
Ignition coil B primary or secondary circuit malfunction
|
| P0353 |
Ignition coil C primary or secondary circuit malfunction
|
| P0442 |
Small leak in EVAP (evaporative emission control) system
|
| P0500 |
Vehicle speed sensor malfunction
|
| P0606 |
PCM (Powertrain Control Module) or ECM malfunction
|
| P0650 |
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) control circuit malfunction
|
| P0654 |
Engine RPM output circuit malfunction
|
| P0656 |
Fuel level output circuit malfunction
|
| P0706 |
Transmission range sensor circuit range fault
|
| P1108 |
Dual alternator battery lamp circuit malfunction
|
| P1794 |
Battery voltage circuit malfunction
|
| B1203 |
Fuel sender circuit short to battery
|
| B1927 |
Faulty passenger side airbag
|
How to explain an OBDII DTC code
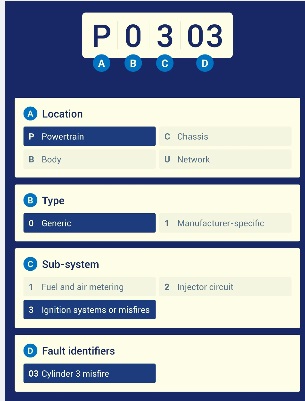
An OBDII DTC comes with five characters and each shows certain faults related for the vehicle
The first character is the identifier of the system that shows locations.
- P: Powertrain that comes with engine, transmission, fuel
- C: Chassis, brakes, suspension, steering
- B: Body, airbags, HVAC, door controls
- U: Network, communication between faults
The second character shows the code type:
- 0: Generic, SAE‑standard code used for manufacturers
- 1: Manufacturer-specific, unique to certain vehicle makers
The third character is the subsystem indicator that shows the subsystem where the error exists, like
- 1 fuel and air metering
- 2 the injector circuit
- 3 ignition systems or misfires
The fourth and fifth are specific fault identifiers, which:
- Range of 00-99
- Pinpoint faults in the vehicle, such as 01, which shows a misfire in cylinder 1 of the engine.
According to the above details, we can show that OBD code P0301 indicates a misfire in cylinder 1 of the vehicle’s engine.
We have another example of a complete code: P0782
- P means ‘powertrain’.
- 0 Means: Generic,
- 7 Means: Transmission,
- 82 Means 2-3 shift malfunctions.
Suppose we have DTC code P0420.
Here we have solved the DTC code p0402.
- P: is an error with the powertrain of the vehicle or the fuel system
- 0: is used for all OBD-II-supported vehicles
- The number “0” means it applies to all OBD-II compliant vehicles.
- 4: shows auxiliary emission control malfunctioning
- 20: There is an error with the vehicle’s catalytic converter.
If your vehicle has the P0420 code, that means there is an error with the catalytic converter. oxygen level is less than the required thresholds and causing emissions in the air.
How to explain J1939 DTC code
SAE J1939 standard is used for heavy-duty trucks. it also applicable for buses and framing trucks.
A J1939 code has 4 fields that give details about DTC:
Suspect Parameter Number (SPN)
- SPN diagnostic fault code that is given through SAE for a certain component or electrical subsystem. It helps to find error locations. It is used for identification errors through the Controller Application (CA).
Failure Mode Identifier (FMI)
- FMI identifier also has errors and comes with sensor short circuits, abnormal rates and calibration errors.
Occurrence Counter (OC)
- OC shows the occurrence of errors. When an error is detected, the OC number increases with each error.
SPN Conversion Method (CM)
- CM explains byte configuration in DTC and shows handling of SPN and FMI. It is used for older types of diagnostic protocols.
Read also Main Symptoms Of a Bad Timing Chain
How to Clear DTC Fault Codes
Follow these steps for DTC fault code clearance.
- First of all, find the OBD port existing below the dashboard on the driver’s side, close to the steering column. If it does not exist, use the manual for finding accurate locations. Connect the OBD scanner tool in this port.
- No power to the OBD scanner tool. There can be a need to use the vehicle VIN or use the vehicle make and model for scanners, based on scanner types.
- For retrieving DTC on the vehicle’s onboard computer, use the ‘Read codes’ option of the scanner; some scanners can have different options.
- Now check the details of alphanumeric DTCs shown on the scanner screen; each code shows different letters and numbers that give different details for errors and their exact locations.
- Now follow the manual of the scanner or the manufacturer’s database to explain the DTC received and the errors shown through codes.
- Keep a record of DTC for future use by taking a print or scan.
- There is an option that exists on the onboard computer of the vehicle for removing DTC based on scanner features and errors detected.
- Solve errors that affect the vehicle, and get services from a technician according to the types of error and complications indicated through DTCs.
- In the last, do follow-up checks through checking DTC for providing accurate problem resolution.
People also ask
What do DTC codes mean?
DTC codes are called engine fault codes that give details for finding and solving errors in vehicles. If there is an error in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system, it gives a DTC code for indications of faults.
What is the 5-digit DTC code?
- DTC is a diagnostic trouble code that is defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers. the code made through the onboard diagnostic system of the vehicle. 5-digit DTC denotes certain errors.
How do I erase permanent DTC codes?
- Permanent DTC can be stored until the vehicle’s onboard system makes sure that the error is solved with normal driving conditions. For clearing code, follow these points:
- First of all, find the main error; make sure that the original error-triggering code is accurately repaired.
- Run the vehicle through a drive cycle according to the manufacturer’s requirements. Accurate finishing helps the system to make sure the repair is performed and the code is clear.
What is DTC in a car?
- DTC is a method used for vehicle diagnostic trouble codes. This code exists on the vehicle’s OBD system and is used for finding errors in the vehicle’s different systems.
- Mechanical uses DTC for finding faults and their solution