Compression springs are open coil helical springs wound to create hindrance compression over the wind axis. Helical compression is a common metal spring design. These coil springs operated independently way that is assembled over a guide rod in a hole. When we apply a load on a compression coil spring, it becomes short and pushes against the load and back to its real length.
Compression springs provide resistance for linear compressing forces, and they provide effective energy storage. Here we will cover details for features, materials, and types of compression springs. Let’s get started.
What is a compression spring?
- The compression spring is made with the use of round spring wire, and its design is a helical coil. It has adjacent coils with pitch that configure length.
- The purpose of the compression spring is to store and release elastic energy in its compressed form.
- It also absorbs shock between two surfaces. Compression springs are made for working with compressive load.
- Compression springs are compressed in load conditions, store elastic energy, and release to their original uncompressed length.
- Its helical coil design provides resistance for compressive forces and best option to use where working is based on resistance.
- This spring is used in vehicle suspensions, medicals, and robots.
- It is also used in AI robots for high-technology medical components.
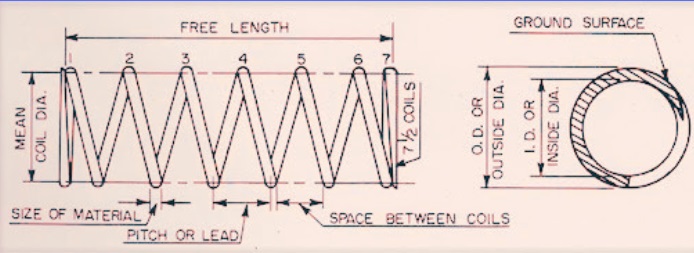
Features of Compression Springs:
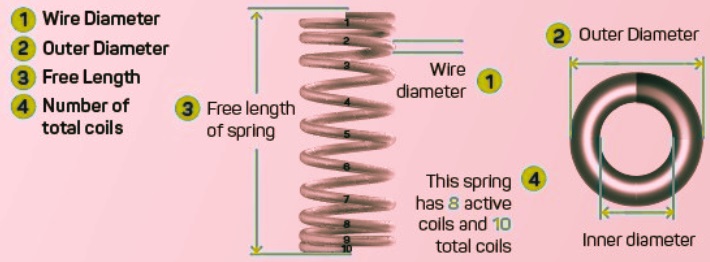
Wire Diameter:
- The spring wire diameter is measured from one side of the wire to the other side of the wire.
Outer Diameter:
- The outside diameter of the compression spring is taken from one side of the external diameter to the adjacent side of the external diameter.
Mean Coil Diameter:
- This value is taken from external diameter to internal diameter. The good technique for meaning mean diameter is to subtract one wire diameter from the external diameter. That provides the mean coil diameter of the spring.
- Mean coil diameter used for measuring spring rate and compression spring stress.
Inner Diameter:
- The inner diameter of a compression spring is measured from one internal side of the inner diameter to the adjacent side of the inner diameter.
Free Length:
- The length of compression in the uncompressed condition is called the spring length.
Total coils:
- • The total amount of helical wound coils that comes with pitch and not having pitch in a compression spring is the net coil of the spring.
Active Coils:
- Helically wound coils that come with pitch for extrusion energy in spring-compressed form.
Solid Height:
- This height is defined as the point where all wires in the spring are in contact and no extra forces are applied through the spring. It is also called coil bind height, where spring coils make a connection with each other and the spring does not have more compression.
Dimensions of Compression Spring
For measuring a compressing spring, we can use a micrometer, dial caliper, or ruler. These parameters are measured for the dimensions of the compressing spring.
- External diameter is measured by putting dial calipers on the external side of the coil width.
- Internal diameter is the width of the inside of the coil spring diameter that is taken from the helix center. In some conditions, internal diameter is difficult to measure. We can measure internal diameter as I.D. = O.D. – 2d. 2d is 2 wire diameters.
- Free length is the uncompressed spring’s full length. For this length, put the caliper on the full length of the spring.
- Wire diameter is measured by putting a caliper on the wire in the middle of the spring.
- Net coil count is explained as a complete rotation and the remaining part of the last coil.
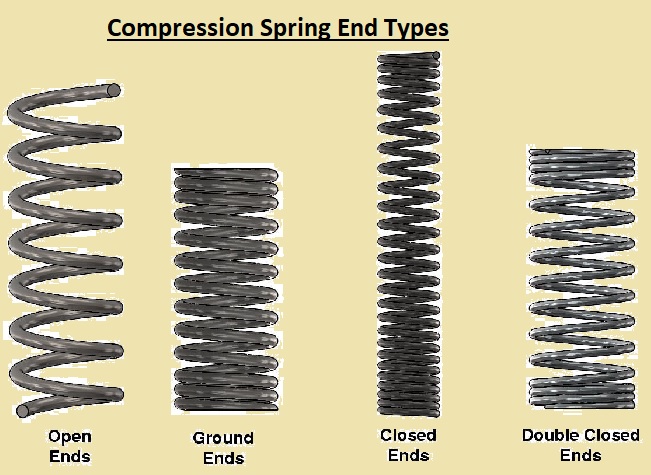
Compression Spring End Types:
Compression spring end types are important for providing accurate spring fitting and working in assembly. The common types of compressing spring end types are as follows.
Closed and Squared Ends:
- This end provides a flat surface design without grinding and is good for springs having a slenderness ratio not more than 3/5. Closed and squared ends provide stability features and minimize the chances of damage in case of high load. It is good for applications where a 3.5 compression spring slenderness ratio is used and provides vertical support.
Closed and Ground Ends:
- The spring-end grinding provides an accurate and flat surface area that provides proper connection with the load. This end type is used for highly precise applications where uniform load compression is needed. It is also part of vehicles and the manufacturing industry. Closed and ground ends are used for springs having a slenderness ratio of more than 4.
Open Ends:
- Springs having open ends have uneven ends after cooling. The main feature of open-end is that we can get more travel as a result. Open-end does not have dead coils on the ends and provides more travel through the solid height space. It is good to use where end accuracy is not important; it is a low-cost option without
Double Closed Ends:
- In this type, both ends of the spring are closed without grounding, which provides high vertical stable features with resistance for lateral forces. This end is good where spring is aligned with low guidance. Double-end gets more solid height with stability.
Triple or more closed ends:
- Custom hybrid options come with more features, such as fine wire diameter springs with dimensions of .005 to .025 thousandths of an inch. In this type compression spring comes with a fine wire diameter, and a larger spring index requires more stability for the compressed spring.
- Multiple closed ends on one side of the spring are used for threading the spring’s internal diameter on the threaded bolt. Different closed ends provide strong assembly over thread. The spring wire diameter synchronizes with thread size also the compression springs’ internal diameter coincides with the bolts’ external diameter for accurate fitting.
One Closed End and Multiple Closed Ends:
- This type comes with one closed end and different closed ends on the other side of the compression spring. This end provides high stability on the spring’s closed end on the upper part of the spring. This end ground for accurate flat surface providing high stability.
Read more:Socket Wrench vs Ratchet: Differences
How to Measure a Compression Spring
- First of all, measure the spring diameter to about 3 decimal places for accuracy with the use of a caliper.
- Get the value of the external diameter of the coils, which can be different based on the coils; select the highest value measured.
- Take the value of the length in the uncompressed condition.
- Check the number of coils; that also shows the revolution count to the closest 1/8th.
- Define the winding direction of coils; in some applications, check surrounding components where they need to spring in a certain direction.
- Find the type of spring; compression springs come with ends ground or non-ground, and end coils can be open or closed.
- Define spring wire material types; if the wire does not have an attraction for the magnet, it is a metallic alloy that requires proper identification. After knowing materials, they are fine working in different conditions like high or low temperatures and the existence of corrosive materials.
Compression Spring Wire Material
Music Wire (ASTM A228):
- This material provides high tensile strength and is best to use for spring features with high load capacity and also has good fatigue resistance. It is good to use for applications where acute accuracy is needed with strength.
Stainless Steel 302
- It provides high resistance to corrosion and is part of applications where springs are connected in corrosive conditions. It is also used for food industry machines and medical devices with durability features.
Hard Drawn (ASTM A227)
- It is a low-cost material, used where material strength is an important factor with low corrosion features. It is normally used in industrial machines.
Compression Spring Plating Types
Plating and finishes of compression springs make them look good but also provide resistance to corrosion. Commonly used spring platen types are
Zinc Plating:
- It has high resistance to corrosion with matte chrome color features and is good to use for spring in humid conditions. Zinc plating also gives a clean look and protection from rust.
Black Zinc:
- It is black in color, has good corrosion resistance, and is best to use for outdoor conditions. Black zinc plating also has a clean look with rust protection features.
Black Oxide:
- It is black matte that is used for reducing light reflection, and black oxide also has resistance to corrosion and controls friction between coils, and best for applications where a highly corrosive environment exists.
Gold Iridite
- It not only has resistance to corrosion but also good electrical conductivity and is good for electronic material uses. The gold iridite finish is used for connectors and is reliable for performance-based applications.
Nickel Plating
- It has a shiny silver chrome look and conductive nature. It has good appeal.
Copper Plating
- It is a copper-like color that is used for springs that needed conductive and is best for electrical connections.
Gold Plating:
- 14K gold electroplating is used for high electrical conductivity compression springs. That plating needed compressing springs on a copper wire necklace on a rack for gold electroplating, which is high cost but has greater conductivity.
FAQs
Define compression spring.
- • A compression spring is an open coil helical spring wound for opposing compression over the wind axis. Helical compression is a common type of metallic spring. These coils are spring-operated independently and are assembled on a guide rod.
How does a compressed spring work?
- The compressed spring produces linear force. That force is generated when weight is applied to the upper or lower part of the spring. It comes in different types, like conical compressed spring and barrel compressed spring.
Are compression springs strong?
- The compressing spring resistance and force-bearing features like strength, stiffness, and spring rate are based on material strength and manufacturing process.
Define the difference between a pressure spring and a compression spring.
- tension and compression Springs come in helical coiled spring designs, and the difference is their working and uses. Tension springs are used for the connection of components, and compression springs keep components apart.
What are the limitations of compression springs?
- Compression springs’ main drawbacks are limited working life, buckling chances, more components, and customization difficulty.
What are the features of a compression spring?
- Compression springs provide resistance for linear comprising forces and have high energy-storing features. Energy stored in a compression spring is defined by material features, coils, and the diameter of the wire.