Graphite is a common allotropic form of carbon. It is a stable allotrope of carbon, and it is part of electrochemistry. It comes in hexagonal crystals, scales, masses, or flexible sheets. With applications of high pressure and temperature, it converted into diamond. It comes with a grainy texture. In this post we will cover details for graphite and its features.
What is Graphite?
- Graphite is produced through the application of high pressure and heat to carbon through Earth’s crust and upper mantle.
- Graphite is seen in pencils, and lead infill comes with graphite and clay.
- Naturally, we can get graphite in metamorphic rocks, such as schist, gneiss, and schist.
- It provides features of metal and nonmetal and is also part of different industries.
- It is the main part of lubricant, and its chemical structure is like diamond, which is pure carbon.
- Graphite is found in China, India, and North Korea. It exists in soft form in nature and cleaves also with low pressure, and it has low specific gravity.
- Its common color is grayish; it also comes in black.
- It is a good conductor of heat and has features to handle high temperatures.
- It is inert, which means it does not react with reagents and acids.
- Graphite comes in three main forms: crystalline, flake, and amorphous, based on mineral type.
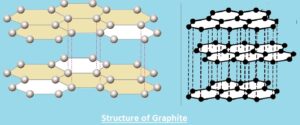
Structure of Graphite
- Graphite is made with carbon atoms connected in layers that form a hexagonal lattice that has 6 members. Rings are connected at edges, and layers of fused rings can be shown as an infinite succession of fused benzene rings.
- In rings, arrayed carbon atoms are sp2-hybridized.
- Each carbon atom in the sp2 molecular orbital model is configured with 3 other species, 3 other carbon atoms.
- • The bond angle between the neighboring carbon atoms in this bonding design is 120 degrees.
- This ring array is made with different carbon atom sheets, and individual sheets are called graphene layers. In the layer plane, the carbon-carbon bond length is 1.418.
- Graphene layers are parallel layers with the “C” crystallographic axis of a hexagonal 4-axis design where graphite crystallizes.
- Carbon atoms in each layer are configured in a honeycomb lattice through a bond length of 0.142 nm, and a plane spacing is 0.335 nm. The distance between layers is 2.5 times the space between atoms of each layer.
- The carbon atom is the first layer aligned with the the carbon atom of the 3rd layer. same as the 2nd layer, carbon atoms are configured with atoms of the 4th layer. that is called the ABABAB” structure.
discovery of graphite
- Graphite was first accidentally made by Edward G. Acheson when he was working with carborundum at high temperatures. During his working, he found about 5150 degrees Celsius silicon in carborundum evaporates, and carbon exists in graphite form.
- for manufacturing graphite Acheson was given a patent in 1896, and in 1897, further production of graphite started.
Graphite Physical Properties
Electrical Conductivity
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity since it has free electron movement that can move to different locations. Its conductivity is also larger than diamond’s.
Thermal Conductivity
- Graphite is also a good thermal conductor since it has a low coefficient of thermal expansion. but diamond is a better thermal conductor than graphite.
Melting Point:
- It also has a high melting point of about 3500 degrees.
Lubrication:
- layers of atoms in graphite has weak forces that help one layer to move over another. in the resulting structure sliced over plane lines. It makes black lead pliable.
Density:
- Its density is 2.26 g/cm³ due to larger spaces between layers, but its density is less than diamond.
Luster
- Graphene comes with delocalized electrons that easily move at different levels of the graphene lattice and reflect light that collides on them. Its surface is lustrous due to reflection being specular as compared to dispersed.
Insoluble:
- It is not highly soluble in organic solvents and water since it has low attraction forces between solvent molecules and carbon atoms.
| Composition | Carbon |
| Color | Dark gray to black |
| Streak | Black gray |
| Luster | Metallic to dull |
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal |
| Cleavage | Basal in direction 1,1 |
| Melting temperature | (3550°C) |
| Density | 2.26 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 1 to 2 Mohs |
| Fracture | Conchoidal |
| Name | Originating from the Ancient Greek graphene |
Chemical Properties of Graphite
The chemical features of graphite are a steel gray to black color, a specific streak, perfect cleavage, and opaque diaphaneity.
Mohs hardness for graphite is 1 to 2, and specific gravity is 2.1 to 2.3.
Types of Graphite
Natural Graphite
Natural graphite is a mineral type of graphite. It comes with different crystallinity features. Normally commercial graphite comes from mines and also comes with other combinations of minerals. When we get graphite from mines, it faces different processes, such as froth flotation for graphite concentration.
Natural graphite has good conductive features for heat and current and can handle these parameters for high temperature. Its melting point is 3650 degrees. It is used for refractories, the steelmaking process, brake linings, and foundry facings.
Natural graphite comes in three types that are processed with the use of natural graphite materials. Each type comes with certain features.
Crystalline Graphite
Crystalline graphite is a rare type of graphite and is high cost with high quality. It is made with direct composition of solid graphic carbon with the use of underground high-temperature fluids like crude oil and transformed into graphite through facing high temperature and pressure.
Crystalline vein graphite is only made in Sri Lanka. Crystalline graphene can be transferred into different shapes and made into solid shapes without the use of a binder additive and reduces the cost for low-quality raw materials.
Crystalline vine graphite cracks normally come with a thickness from one centimeter to one meter and are of a higher pure form than 90 percent CG. It provides 95 to 99 percent carbon without refining.
Amorphous Graphite
Amorphous graphite mad with connection of metamorphoses between anthracite coal seam and metamorphic agent. that make microcrystalline graphite that also called amorphous graphite.
amorphous graphite is limited graphite type in natural graphite. based on locations graphite content is 25 to 85 percent. it exists in small size, crystal like shape in col, stale conditions. low carbon purity in range of 70 to 85 percent carbon in refined form. For its proper vision magnification used.
it is part of quality graphite products like lubricants, refractories, paints, and brake pads
Flake Graphite
natural flake graphite is made through carbon when faces high pressure and temperature. the carbon materials comes in organic or inorganic form, and some comes in flake graphite that is taken from organic deposits.
pressure needed is higher than 1 gigapascal and temperature needed more than 800 degrees. flake graphite is exist in metamorphic rocks that are distributed on ore body. range of carbon concentration in range of 5 to 40 percent.
flatek graphite is exits in lamellar or flaky shape in some metamorphic rockes like gneiss, schists.
foam flotation used for extraction flake graphite. floating graphite comes with graphite material about 80 to 90 percent. more than 98 percent of layers made with use of graphtie chemical preparation process.
Synthetic Graphite
Synthetic graphite is made from coke and pitch. It is not crystalline like natural graphite. It comes with arranged pyrolytic graphite or accurate direction pyrolytic graphite with angular spaces between graphite sheets of less than one degree.
There are two types of synthetic graphite. One is electrographite, pure carbon that is made from coal tar pitch and calcined petroleum coke in an electric furnace.
other types of synthetic graphite that are made with calcined petroleum pitch up uptop 2800 degrees.
Synthetic graphite has high electrical resistance and porosity features and low density. It provides high porosity and is not used for refractory uses.
Synthetic graphite comes with graphite carbon that gets through the process of graphitization, heat treatment of non-graphitic carbon,
It is used in the aviation industry, carbon brushes, graphite electrodes, and batteries made with graphite.
What is graphite used for?
Writing Materials
- The word “graphite” means “to write.” That’s why it is commonly used for graphite in lead pencils. Lead is a mixture of clay and graphite that comes in amorphous form.
Lubricants
- Graphite is the main component in lubricants such as grease. It reacts with atmospheric water vapor and makes a thin film on the surface and minimizes friction. Graphite is also part of clutches and car brakes.
- In powdered form, graphite is used in paints.
Refractories
- It works as a refractory since it handles heat and is not affected by heat. It is used in the manufacturing industry and to make glass and steel.
Nuclear Reactors
- It is used in reactors for stabilizing the nuclear reaction since it has features to absorb neutrons.
Electrical Industry
- crystalline flake Graphite is part of carbon electrodes, brushes, and plates that are part of dry cell batteries and the electrical industry. Natural graphite is also processed to make synthetic graphite.
Electrodes
- It is used in different electrodes, carbon brushes, electrical contacts, rheostats, discs, rods, etc.
Atomic Energy
- Graphite is also part of nuclear energy; in this process, pure graphite is used as a matrix enclosing uranium metal bars. Graphite matrix work as a moderator that controls high-speed neutrons in an atomic pile for the required value of resonance capture through uranium atoms (U238) and then converts into plutonium (Pu239).
FAQs
Is graphite used in pencils?
- Slippery sheets make graphite sloppy and help to write content. The particles of the carbon sheet rub off the pencil center and onto the page. These features make it good for dry lubricant for graphite powder.
Where is graphite used?
- It is used in lubricants and pencils and provides high heat and energy. It is also used for electrodes, batteries, and solar panels.
Is graphite made entirely of carbon?
- Graphite is an allotropic form of carbon that comes with a completely carbon component. In graphite, carbon atoms are configured and mixed in a configuration to make a crystal layout. that provide certain types of features
Is graphite a stone or a metal?
- Graphite is a nonmetal that shows metallic features. It is a good conductor of heat and current and comes with high natural strength and stiffness of material. It has features to provide high strength and a stable design for temperatures more than 3600 degrees and also resist chemicals.
Is graphite a rust?
- Graphite is an inert material. that has resistance to corrosion and other chemicals like acids, bases, oils, and metals. Graphite is corrosion resistant to acids and solvents. It comes with limited resistance over oxidizing medium and bases.
Is graphite an element?
- Graphite is an element, not a compound, and graphite is a mineral but of an inorganic nature. Element carbon has features to make different compounds than other elements.
Is the structure of graphite tetrahedral?
- Graphite does not have a tetrahedral structure. Graphite is naturally crystalline carbon. It exists in metamorphic and igneous rocks. Graphite is made when carbon faces heat and pressure in the crust part of the earth and the upper mantle.
Is graphite a good conductor of electricity?
- Graphite is a good conductor of heat and current. since it has a molecular structure that helps electrons to move freely.