Piezometers are geotechnical sensor devices that help to measure pore water pressure in the ground. It is made for measuring pore water pressure in soil, foundations, earth fills, and concrete structures. It is an important tool for geotechnical monitoring systems.
In this post, we will cover detailed features for piezometers and related factors. Let’s get started.
What Is a Piezometer?
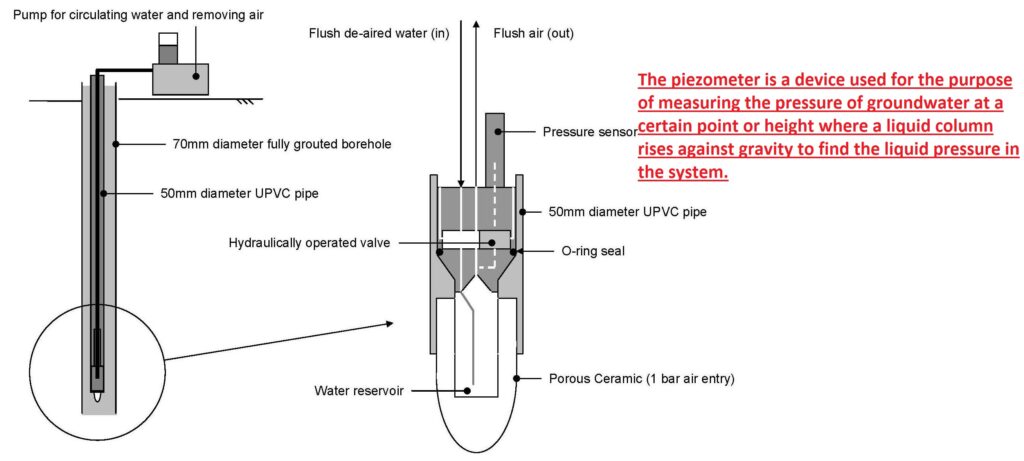
- The piezometer is a device used for the purpose of measuring the pressure of groundwater at a certain point or height where a liquid column rises against gravity to find the liquid pressure in the system.
- The piezometer is not physically put into fluid like a pitot tube, but it has features to detect static pressure.
- It needed manual reading and observation to provide water level details in the information.
- Automated reading of different electrical pressure transducers makes data acquisition easy.
- Standpipes put into aquifers are the first example of piezometers used for geotechnical engineering.
- That, also called a Casagrande piezometer, comes with a slotted casing in the zone where water pressure is measured.
- To avoid surface water polluting the groundwater supply, casing is sealed into the drill hole with the use of concrete or clay.
- The water level in the piezometer does not properly match the water table in the unconfined aquifer in case of required vertical component flow of velocity.
- The water level of the piezometer compared to the water table is a good sign of aquifer pressure in a limited aquifer in artesian conditions.
- The five-centimeter-diameter standpipe is used for piezometer wells, which have a smaller diameter as compared to production wells.
- For monitoring groundwater pressure at the installation area, piezometers are pushed into the ground with sturdy casings.
- The transducers that transform pressure into electrical signals can be strain gauges or pneumatic.
What is the need for a piezometer?
The main motive of the piezometer is
- It helps to find the water effect in the pores of soil or rock for minimizing load-bearing features of soil. The effect is highly pronounced through high pore water pressure, causing net damage for the load-bearing capacity of soil
- The piezometer is used for groundwater monitoring to find the level and flow layout of groundwater.
- It also helps to find the flow pattern of water in rock fill and concrete dams and also delineate the phreatic line.
Parts of a piezometer
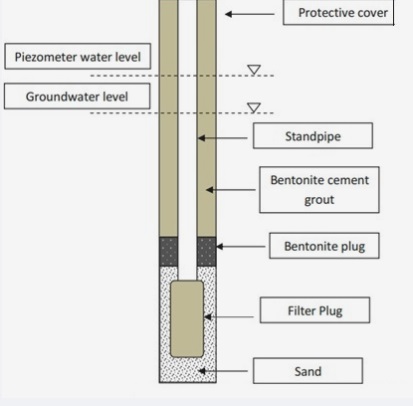
- The piezometer comes with porous stone or a perforated pipe and a plastic standpipe. For piezometers, normally open standpipe piezometers are also used.
- The pipe connected in the borehole, and the porous part is designed for measuring porous values.
- The annulus between the porous filter and the bare hole exists, covered from sand and sealed from both sides.
- The groundwater pressure sends water to the standpipe until the standpipe has the same water level as the piezometric level in the ground, compared to the elevation of the porous filter.
Types of Piezometers
Casagrande or Open Standpipe Piezometers
- The basic tool used for measuring piezometric level in the ground is the open standpipe piezometer. That is a plastic-made pipe that comes with a diameter of 20 mm and a porous part at the lower side.
- The pipe is connected to the inner side of the borehole, and the porous part is placed lower, where the piezometric level is measured.
- The annulus existing between the porous filter and the borehole comes with sand and is sealed with bentonite on both sides, and the remaining borehole is filled with cement mortar.
- Groundwater pressure sends water into the standpipe till the water level in the standpipe is the same as the piezometric level in the ground at the porous filter elevation.
- In this way, the piezometer water level is monitored and used.
Electric Piezometers
- Electric piezometers come with a deflecting diaphragm and a porous filter parted with a small water reservoir. The vibrating wire used for measuring the deflection of the diaphragm. The piezometer-calculated values are transformed into equivalent pressure with the use of an accurate calibration process.
- The next process is the same as opening standpipe piezometers. The electric piezometer is put into the borehole, and the annulus between the porous filter and the borehole is filled with bentonite grout.
- Water from the ground pushes due to buoyant force in the reservoir and deflects the diaphragm until the pressure in the reservoir is similar to the pore water pressure value in the ground at the porous filter elevation.
- If we connect an electric piezometer over the current groundwater table, pore pressure in the soil is negative, and water in the piezometer gets from the reservoir. In this condition the piezometer has air and causes dysfunction.
Hydraulic Piezometers
- It comes with a porous filter that has a reservoir of water, separated from the pressure gauge through resilient and water-filled tubes.
- These tubes cause water to flow in the system to remove air and fill the reservoir with water.
- A piezometer measures total hydraulic pressure, which helps to measure pore pressure.
Pneumatic Piezometers
- This type of piezometer operates with gas pressure; it is used for boreholes, fills, or for larger diameter standpipes. Values are measured through a pneumatic indicator.
Vibrating Wire Piezometers
This type of piezometer is used for measuring pore water pressure in completely or partially saturated soil and rock. This type of piezometer comes with different parts that are
- It has a sensitive stainless steel diaphragm, a magnetic high-tensile-strength stretched wire, one end of which is anchored and the other fixed with the diaphragm.
- Ceramic low air filter and a thermistor are used for measuring temperature
- It has a glass-to-metal seal with 4 pins for making a cable connection and a stainless steel casing that has corrosion resistance and impurity resistance found in under-field conditions.
Piezometer working
- The vibrating wire piezometer comes with a magnetic high-tensile-strength stretched wire where one side is anchored and the other is fixed with a diaphragm that deflects when pressure is applied.
- Piezometer working is based on pressure variations. The changes in pressure deflect the diaphragm in direct relation, and this deflection affects the tension in the stretched wire. Changes in pore pressure have an effect on the tension of the wire.
- Wire plucked with coil magnet: according to the proportion of tension in the wire, it resonates at frequency f that can be measured as
f = {[σg/ρ] ^1/2}/ 2l Hz
- σ = tension of the wire
- g = gravitational constant
- ρ = density of the wire
- l = length of wire
The resonant frequency that helps wire to vibrate, induces AC in the coil magnet. that define the piezometer equations
Pore pressure has a direct relation with the square of frequency
PIEZOMETRIC MEASUREMENT Techniques
Using a probe
- The measurements from piezometric are taken care of by a process that needs high accuracy and reliable working. The basic method is to use a manual piezometric probe, which is used for spot measurements.
- It is a simple but less effective method that measures the height of water with the use of a differential pressure sensor. It is good for periodic measurements that measure the value of the water table at a point in time.
Remote transmission
- The piezometer is configured with an automatic recorder that helps data collection with tools for retrieval at a distance. The main features are that it provides real-time monitoring, reduces the use of field visits, and gives complete and dynamic details of variations in aquifers.
- Due to automatic sensors and remote transmission, it is good to monitor changes in water levels in real time, give detailed values of hydrological cycles, and affect human work on groundwater.
- Remote transmission helps to integrate piezometry data in the detailed system and helps to analyze and manage water resources easily and effectively.
Piezometer Installation Proccess
Follow these points for installation of the piezometer.
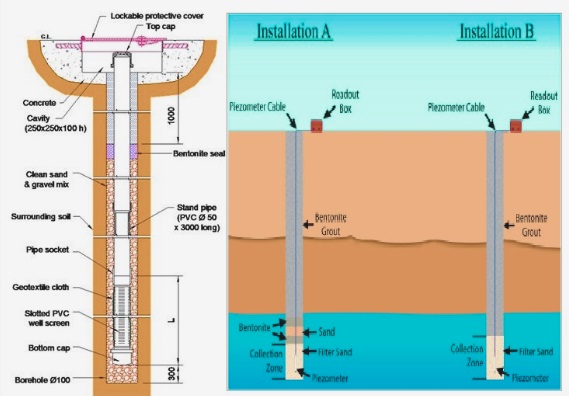
- The standpipe is configured in a borehole that is drilled in soil at a defined depth for intercepting groundwater.
- The slotted pipe is configured through a socket to the same dimension plastic standpipes set to the surface.
- The borehole is filled with pea gravel, and the upper part of the borehole is sealed with a cement-bentonite plug.
- Groundwater seeps into the standpipe with a slotted point and gets the groundwater level. That level was defined with electrical sounding devices like EPP-10/6 lowered to the surface.
- The plated hinged cover, through locking features, comes for mounting at the upper part of the standpipe.
- Locking features come with a universal key and dust protection cap.
Monitoring Wells vs. Piezometers
- Shallow monitoring wells and piezometers are different from each other. They are pipes that are used for measuring the level of water below ground when the water level increases or decreases.
- Shallow monitoring wells come with perforations in the pipe length beneath the ground; as a result, the pipe can easily access water in the groundwater table.
- Shallow monitoring well measured pressure of water over pipe height. Some use well monitoring for this feature.
- Shallow monitoring wells, also known as observation wells, are perforated pipes.
- The piezometer does not measure water column height in the complete borehole and measures groundwater height at the lower end of the pipe.
- A piezometer, also called a cased well, is defined as a shallow monitoring well and piezometer since it helps to measure certain values of parameters.
Advantages of Piezometer
- It is used for measuring rock and soil performance.
- It has an easy design and a reliable nature for measuring fluid static pressure.
- It is used for pore water pressure level measurements.
Disadvantages of Piezometer
- It is not used for measuring static pressure for gases since it does not face free surfaces.
- It is not good for measuring vacuum pressure since air comes in the vessel.
- It is not for high pressure in low-weight liquids since it has a high piezometric head and is difficult to handle.
FAQs
What are the uses of a piezometer?
- The piezometer is a tube that comes with an open lower part that is used for finding the depth of groundwater by drilling into the ground at different depths. It is also used for measuring the depth of water in a tube for finding the direction of flow in both horizontal and vertical way.
What is a piezometer tool used to measure?
- A piezometer is a tool that is used for measuring pressure head in a pipe, tank, or soil. For pipes and tanks, it comes with small pipes and tubes. One end is connected through the wall of the pipe where the valve is located.
What is a piezometer also called?
- Piezometers, also called pore pressure meters, are transducers used for pressure that are connected below ground to measure the subsurface piezometric level in groundwater level, rock, and soil.
What is the difference between a piezometer and a pressure gauge?
- A piezometer is a normal tube that is configured at 90 degrees with a liquid system where pressure needs to be measured. The pressure gauge is applied for measuring fluid density and also set and operates the fluid power machine.
What are the different types of piezometers?
- The commonly used types of piezometer are the standpipe piezometer, vibrating wire piezometer, and pneumatic piezometer.
What is the function of a piezometer?
- A piezometer is a tool used for measuring the pressure of groundwater in pipes, dams, and conduits. It is monitored and regulated through excavation, boreholes, or drainage.

Hey there! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4!
Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts!
Keep up the excellent work!