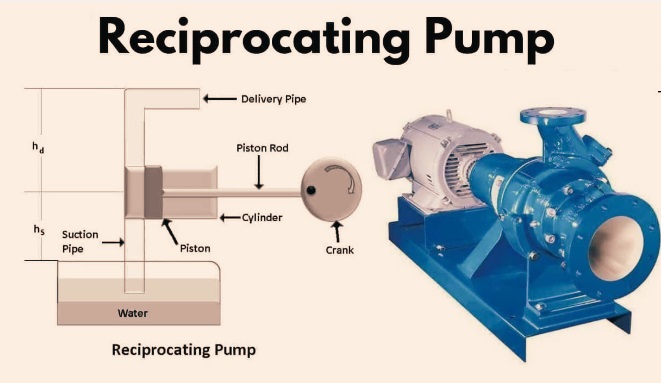
A reciprocating pump is basically a positive-displacement pump that stores or captures moving fluid in a cavity and then releases a certain amount through mechanical pressure. It is a constant pump that operates at low flow speed and high discharge pressure conditions.
In this post, we will cover the detailed features of the reciprocating pump and related factors. So let’s get started.
What is a reciprocating pump?
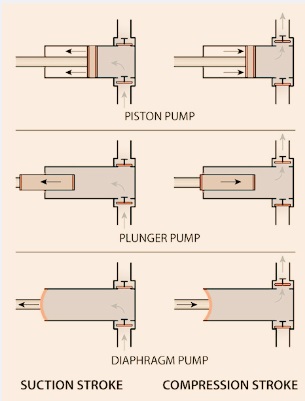
- The reciprocating pump is a type of positive-displacement pump that comes with a piston pump, a diaphragm pump, and a plunger pump.
- If it has proper maintenance and working conditions, a reciprocating pump will work for many years.
- If improperly maintained, the pump causes wear and tear. It is used where small liquids are handled and high-pressure transmission is involved.
- In this pump chamber, which holds liquids is a static cylinder that comes with a piston or plunger.
- A reciprocating pump employs back-and-forth piston motion, a plunger, or a diaphragm.
- This repetitive movement, called reciprocation, is a process where fluid flows through the pump.
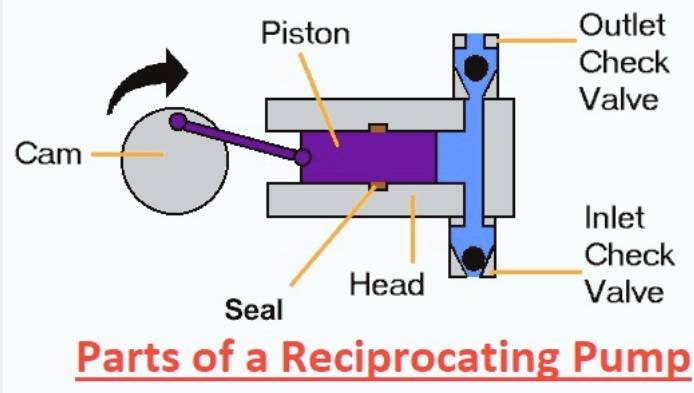
Parts of a Reciprocating Pump
main parts of the reciprocating pump areas
Water reservoir
- It is a component of a reciprocating pump; that is, it is the source from which the reciprocating pump gets water. There can be other fluids existing here.
Strainer
- It comes with impurities of liquid used for choking the pump.
Suction Pipe
- It is a pipe where the pump gets water from the reservoir.
Suction Valve
- It is a non-returning valve connected to the suction pipe and provides flow from the reservoir to the pump.
Cylinder
- It is the main component where pressure increases. It is a hollow cylinder that comes with a coating. It has a piston with piston rings.
Piston or plunger and piston rod
- piston connected with rod or piston rod. This piston rod is then connected with the connecting rod.
- The piston provides reciprocating movement in forward and reverse motion and produces pressure in the cylinder.
Piston rings
- Piston rings are small in size but are the main component that protects the piston surface and also the cylinder’s inner area from damage. It operates the pump in a smooth way.
Packing
- Packing is the main part of pump that provides a strong sealing between the cylinder and piston. It controls fluid leakage.
Crank and Connecting Rod
- • A crank connected with a power supply and connecting rod provides a connection between the piston rod and crank. These parts provide the circulation motion to the linear motion conversion.
Delivery valve
- • The delivery valve is a non-returning type and creates pressure. It provides creation of pressure and protects the pump from backflow.
Delivery pipe
- It provides a supply of fluid to reach a certain point.
Air Vessel
- • A reciprocating pump comes with an air vessel that minimizes frictional head.
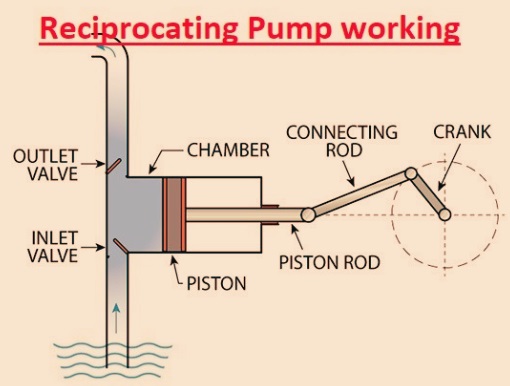
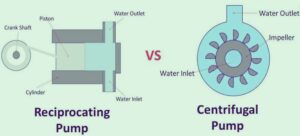
Reciprocating Pump working
- • In the above diagram of a reciprocating chamber, you can see.
- the main parts of the piston, plunger, or diaphragm that operate in the chamber that defines the pump volume.
- The connecting rod is connected with the motor crank at one end and components like the piston and plunger at the second end.
- • The suction pipe helps fluids move into the chamber, and the delivery pipe helps fluids to release.
- Inlet and outlet valves monitor flow inward and outward of the chamber.
- There are two steps involved for working of reciprocating pumps that are
Suction
- The piston plunger is pulled backward, which increases chamber volume and causes a vacuum.
- This process comes with opening the inlet valve and closing the outlet valve. A vacuum working on the chamber releases fluid through the inlet.
Compression
- When the plunger, piston, or diaphragm gets the highest displacement, then moves into the chamber.
- The inlet valve is closed, and the outlet valve gets opened.
- Fluid releases through pressure applications in the outlet.
- suction and compression phases of a reciprocating pump seen here
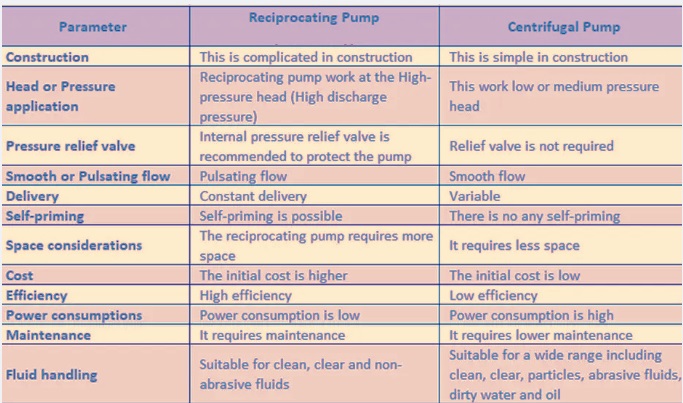
Centrifugal vs. reciprocating pumps
- Centrifugal and reciprocating pumps operate with different functions.
- • A centrifugal pump operated with transformational rotational kinetic energy that is of motor and produces static fluid pressure.
- Flow velocity increases in the impeller, and that energy is transformed into static pressure due to changes in the flow area of the volute section.
- A reciprocating pump is a positive displacement pump.
- Liquid releases at a certain rate per revolution of the pump.
- displacement rate based on plunger diameter, stroke length, and plunger used.
- Reciprocating movement is produced through using the crank and slider process of the pump, resulting in liquid movement and getting energy from the discharge suction.
- reciprocating pump is used for providing high capacity with a fixed volume of fluid since flow rate has a linear relation with speed.
- Variable capacity is achieved through changing pump speed and pressure on the discharge side of the system to adjust to the system.
- We can produce a constant flow irrespective of pressure requirements with the process.
Types of Reciprocating Pumps
There are different types of reciprocating pumps that are explained here.
Piston Power Pump
- This reciprocating pump is defined based on direction, working process, pump components like the plunger, and phases.
- This pump is used with power and pressure washers. It provides high pressure with low volume.
- Piston power pumps come with duplex or triplex units.
- Single-acting pumps apply pressure in one direction of the stroke, and double-acting pumps apply pressure in both directions.
- Piston power pump used on a larger basis.
Metering Pump
- This pump provide easy chemical pastes dispensing and effectively.
- That is done through use of a reciprocating piston.
- The diaphragm method used for metering pumps. In industries and the medical industry, it is commonly used.
- This pumping process comes with adjustable stroke length that helps to set dosage level.
- Metering pumps come in different designs; larger sizes are used for chemical injection in process plants.
- small design used for pharmaceutical filling, adhesive dispensing,
Diaphragm Pump
- This pump uses flexible membranes that control pump cavities. It can be air operated or electric.
- Diaphragm pumps are used for oil transmission and other hazardous fluids.
- It comes with different-sized small portable pumps used for site operations.
- different methods used for actuating this pump, like hydraulic fluid, air
Steam Power Pump
- steam reciprocating pump no transforming rotary motion into linear motion with use of a stem operating piston to power the pump piston.
- Pumps come with double-acting features on both the stem end and the fluid end.
- There is a lever connected with a piston rod that varies steam flow as the steam.
- It occurs when the stem and pump piston get to the end of the stroke.
- Two steam cylinders are mostly used. The API 674 standard pump is used for hazardous areas like petrochemical, oil, and refining industries.
Advantages
- reciprocating pumps have features to generate high pressure, and the model produces more than 69 MPa (10,000 psi)
- It also comes with a fixed fluid displacement volume at a certain speed that helps it to work well for low flow, like metering and dispensing.
- Reciprocating pumps have features to handle high-viscosity fluids like oils, paints, and resins.
- It has features to handle solids and fluids that corroded parts of the high-speed rotary pump.
- Diaphragm pumps used for aggressive chemical handling
disadvantages
- produces pressure pulsations with reciprocating motion. Pulsation dampers are connected for avoiding damage to the pump and the surrounding area.
- It needed costly maintenance.
- It has high cost and viscous fluids difficult to pump.
- It has a low flow rate.
Conclusion
A reciprocating pump is a positive displacement pump that uses a piston for moving fluid in a system through a reciprocating motion. It has high pressure and low flow and is used for oil and gas industries, water treatment, and chemical processing.
It needed more maintenance than other pump types since it has moving parts and high accuracy and performs different operations.
applications
- Reciprocating pumps provide higher highefficinecy, working features, and energy usage than other pumps like centrifugal pumps.
- Reciprocal pumps are used for low flow and high-pressure differential, and centrifugal pumps are low cost due to process liquid viscosity.
- It is used for washing water and high-pressure chemical injection.
- its features lower erosion rate than centrifugal since it has low fluid velocity
- It has high efficiency with near-zero emissions.
FAQs
What do you mean by reciprocating pump?
- reciprocating pumps called positive-displacement pistons that operated with steam cylinders and external power supplies connected with crankshafts.
- It has features for producing high pressure.
What is the difference between a centrifugal pump and a reciprocating pump?
- The basic difference between centrifugal pumps and reciprocating pumps is that centrifugal pumps operate with low to medium pressure heads.
- reciprocating pump operated with high-medium pressure heads.
What are the disadvantages of reciprocating pumps?
- It has a high starting cost and is difficult to pump viscous fluids. It has high maintenance costs since it has larger components.
- It has a lower flow rate than other pump types.
Why is a reciprocating pump called positive displacement?
- Reciprocating pumps are defined as positive-displacement pumps since their mechanism of displacement fixes the volume of fluid for each cycle.
Which faults are common to a reciprocating pump?
- Air or vapor pocket in the inlet line.
- The capacity of the charge pump is less than the capacity of the power pump.
- Air or vapor trapped in or above the inlet manifold.
- Air leak in the liquid supply piping system.
- Loose bolts in the pump inlet manifold.
- Air or gases entrained in liquid.
What is the working principle of a reciprocating pump?
- reciprocating pump operates through the following positive displacement principle: where a piston moves back and forth in a cylinder for producing suction, draws liquid at the time of the suction stroke, and releases it with the discharge stroke through a one-way valve.
- The crank and connecting rod system transforms the rotational energy of the motor into the reciprocating motion of the piston, helping the pump to provide a constant volume of fluid.