Rolling mills are used to roll hot or cold ferrous or nonferrous strips, rods, and wires. According to the type of mill, it is used for hot or cold breakdown and bar finishing, strip. It is also used for finishing rollling of thin-gauge stock or compacting.
Rolling mills are used to fulfill the requirements of different industries and are part of the material research industry for fulfilling different industries. In this post we will cover details and features for different industries. So let’s get started.
WHAT IS A ROLLING MILL?
- For metalworking, rolling is a metallic forming process where metal stock passes through rolls for reducing thickness and, as a result, makes uniform thickness.
- It is like the rolling of dough; rolling is defined based on the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is not according to the recrystallization temperature, this process is called hot rolling.
- If the temperature of the metal is less than the recrystallization temperature, it is called cold rolling.
- For use purposes, the hot rolling process has higher tonnage as compared to other production processes, and the cold rolling process has high tonnage for the cold working process.
- Roll stands, rolls holding pairs, are configured with each other into rolling mills that process metal like steel into products, for example, structural steel, bar stock, and rails.
- Different steel mills come with rolling mill partitions that transform semi-finished casting objects into final assemblies.
Rolling Process Principle
- In the rolling process two rollers push each other and squeeze the metallic component in the middle of them. The distance between rollers needed to be less than the starting thickness of metal. If metal passes through the space between rollers, it will move ahead.
- The rolling process helps to reduce metal thickness and make it thinner, longer, and larger while keeping the net volume the same.
Rolling Mill Parts
There are different parts of rolling mills based on design and type; each performs certain functions.
Rolls (or Rollers):
- It is the main component that applies force on metal in a rolling mill. Rolls are made with different materials like forged steel or cast iron, and rolls are moved for providing accurate shape and surface finishing for final assembly.
Mill Stands:
- It is used for supporting and aligning rolls and provides a sturdy design for holding rolls at the time of rolling.
Bearings:
- It is used for supporting rotating shafts of rolls and provides a low-friction surface at time of working.
Screw-down Mechanism:
- This process sets a gap between rolls for providing a certain thickness level, and this process is hydraulic or mechanical based on applications.
Drive System:
- It comes with motors, gearboxes, and spindles that give power and torque for rotation of rolls.
Guides and Manipulators:
- It defines direction for the working component when it moves through the mill from the entry point to the exit of the roll gaps.
Cooling Systems:
- It is used in hot rolling, like water spray, for dissipation of heat on rolls and working components that minimizes material features degradation.
Shears
- For cutting rolled products to length, shears are used.
Control Systems:
- Modern rolling mills come with a feedback control system with the use of a computer for automated rolling functions, and it monitors at the time of processing and quality control.
Different Terms for Rolling Process
Ingot:
- the initial metal input given to the rolling process, which is extracted from casting at different errors.
Bloom:
- • The initial rolled object, or ingot, comes with a cross section larger than 230 square centimeters.
Billet:
- The object gets through rolling of bloom with a cross-sectional area larger than 1600 mm².
Slab:
- the hot-rolled ingot having a cross-sectional area larger than 100 cm² and a width equal to or larger than double its thickness
Plate:
- The mill outcomes with thicknesses larger than 6 mm
Sheet:
- The mill product comes with a thickness less than 6 mm and a width larger than 600 mm.
Strip:
- The mill object comes with a thickness less than 6 mm and a width value lower than 600 mm.
Types of Rolling Mill
Rolling mills come with tools that move rollers and initiate and end the rolling process. It comes with one or more roller stands, reducing gears, a main drive motor, a stand pinion, a flywheel, and gears. These components operate with each other for complete the rolling process.
There are different types of rolling mills, and each has its own functions.
Two High Rolling Mills
- This type comes with two longer stands and two rolls that are configured on each other. In this rolling mill, rollers move in the reverse direction, and the direction varies after each metallic movement. The metal is pressed again and again and takes about 30 seconds to turn an ingot into a bloom.
Three High Rolling Mills
- This mill comes with three stands and 3 rollers; all are on the same vertical plane. The upper and lower rollers move in the same direction, and the central roller moves in the reverse direction.
- In this mill drive direction does not vary at time of passes. It has higher efficiency and is easier to use than two high rolling mills.
Four High Rolling Mills
- It comes with two backup rollers and two working rollers stacked to each other in a similar vertical plane. The backup rollers come with a larger diameter as compared to the working rollers.
- These rollers are used for sheet rolling; small-diameter working rollers are used for minimizing power used, but they cause the working roller to bend, which results in compressing the sheet in a different direction.
- So backup rollers are used for avoiding rollers bending.
Cluster Rolling Mill
- It is made with two working rollers and also two or more backup rollers. The supported need defines the backup rollers needed. It is mostly used for cold rolling processes.
Planetary Rolling Mill
- Planetary mill comes with medium output that rolls steel strips, and output is less than continuous mills with larger stands, and it is higher than reversing two-high or three-high mills.
- All metals can be rolled using these mills, and their low ductility is advantageous for different uses.
Tandem or Continuous Mill
- For rolling mills that work in continuous groups, vibrations are transmitted from one stand to another through bars and strips. As a result, vibration excitation in one stand causes vibrations in other rolling mills that are in a similar group.
Rolling Process Types
- There are different processes used for metal rolling, and these processes are used for different applications. Product quantity, manufacturing process, and different parameters help to use the rolling process type. The commonly used rolling processes are as
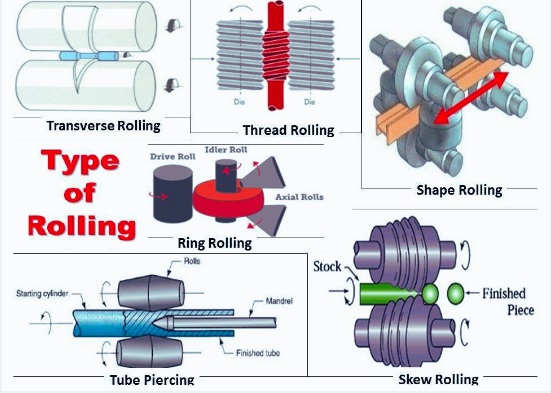
Thread and Gear Rolling:
- In this method metal input with dies rolls and threads. This process cuts threads and gears.
Shape Rolling:
- This rolling method makes metals, Rolls I section, H section, the metal is converted into different shapes with rolls. The final shapes define roller combinations and shapes with high accuracy.
Ring-rolling:
- This type comes with a drive roller, idler rollers, and an axial roller. Drive and idler rollers revolve in similar directions; idler rollers move in metal, and when the hole diameter increases, they come close to each other.
Tube Piercing:
- Two rollers with a static mandrel make this rolling process perform. Metal moves towards the mandrel when the roller moves it. The compression forces of the mandrel result in the metal moving toward it and making a hole. It provides thick-walled hollow tubes.
Skew Rolling:
- Ball bearing rolled with this method, metal passes through certain rollers for making bearing balls. That is an easy method for making ball bearings in bulk.
Transverse Rolling:
- In this process we can get a tapered surface; metal is put between rotating rollers. The roller comes with a tapered part that resulted in surface tapering. It is used at the time of manufacturing of tapered shafts, leaf springs
Roll-bending:
- This process is used for bending metals; if metal passes through rollers, it curves over their direction. Roll bending provides high efficiency for vehicle aerodynamics through bending chassis tubing.
Flat-rolled:
- It is a rolling process used for making blooms and slabs through ingots. Input flat metal is output with low thickness. This method of rolling minzies metallic thickness at output
Controlled Rolling:
- It is performed in a controlled way and is part of industries. For the steel industry, grain size is premade, and rolling is used for making that grain size that is already define
Types of Rolling Mills Based on Temperature
Hot Rolling Mills
- Hot rolling mill is metal that is heated over recrystallization temperature. So metal is ductile and changes shape due to high temperature.
- This provides a larger reduction in thickness from a single pass and is used for the initial breakdown of larger ingots in shapes that are called blooms and billets.
- Hot rolling helps to refine grain structure, remove cast errors, and provide certain design variations, but dimensional accuracy is affected, and the surface is affected due to oxidation.
Cold Rolling Mills
- Cold rolling is a process where metal has a lower temperature than the recrystallization temperature, normally room temperature.
- The main benefit of cold rolling is surface finishes; tolerances are less, and strength increases due to harder work.
- For low-temperature metal has a low ductile nature, needs more deformation forces, and comes with less reduction for one pass
- Cold rolling is used for making sheets, strips, and foils for accuracy and also parts of vehicles or aluminum foils.
Warm Rolling Mills
- It is a middle type of processing normally operated at a temperature that is in the range of hot and cold rolling processes.
- It has features providing some operational features related to hot rolling and good dimensional control and surface finish that get through hot rolling, and it uses low forces as compared to cold rolling.
- This type of mill is used for resulting features that need to be defined as not important hot-rolled features and also not cold-rolled features, like for aluminum foil.
Advantages of the Rolling Process
- It is a high-speed and low-time-taking process that provides a high manufacturing rate.
- It is mostly used for bulk production systems, and it is good for larger-scale manufacturing systems.
- It has high efficiency for material use and energy use.
- It has features for making working components that have complicated designs.
- Rolling process used for getting working components with low tolerances and high accuracy and consistency features
Disadvantages of the Rolling Process
- It has a high initial cost for setting up rolling functions.
- The rolled working component comes with a less refined surface finish and requires an extra finishing process.
- It is good to use for mass production processes but less effective for small-scale productions.
Applications of Rolling Process
- Rolling processs used for manufacturing shafts, rods, axles, and spindles.
- It is also part of making a working component with required cross sections.
- It used to make gear manufacturing through gear blanks.
- It used to make metallic sheet panels and plates,,,, also part the vehiclecle industry
FAQs
Define rolling mill in a steel plant.
- The rolling mill used for rolling sheet metal changes configurations according to name. A rolling mill is used for compressing metal to the required thickness, bending it to certain shapes, and making strips of the required dimensions.
What are the features of a rolling mill?
- The use of rolling mills comes with many features. It has good surface polish, minimizes material waste, and increases the strength of metal and capacity for making larger designs.
How does a rolling mill work?
- For rolling mill 2 rolls slide metals exist, and the compressive pressure applied resulted in the material converting into the designed shape. The outcomes define either a roll move in the same direction or in the reverse direction.
Why is a rolling mill used?
- Rolling mills used for metal compression at constant thickness bent at certain shapes and, as a result, make required dimensions
What are the raw materials of a rolling mill?
- The rolling process is a type of cold forging. Different materials like low carbon steel and galvanized aluminum sheets are used for roll forming.