Have you ever seen the flashiest parts in the workshop that’s called Spark? It can be caused by different metals for sparks, and with the use of a spark test, we can find different features for ferrous metal and use it as a high-speed and low method for the identification of different metals.
Sparks are based on high heat generated from welding or grinding steel through a pedestal, angle, or surface grinder. Here we will cover details for the Spark test and related details.
What is the Spark Testing?
- Spark testing is a process that is used for the determination of types of ferrous materials. It involved the use of a metallic component, like scrap, and the application of a grinding wheel for released spark observation.
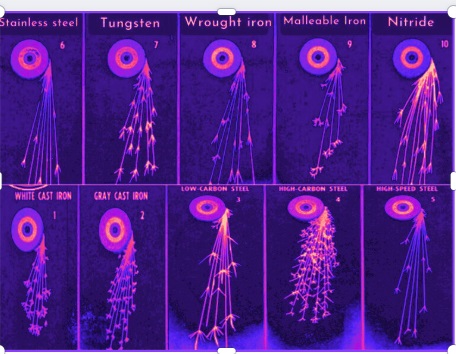
- The emitted spark can be compared with the chart of sparks that were measured for the testing sample to find types.
- Spark testing is also employed for ferrous materials sorting and to make a difference between them.
- The spark testing is a low-cost and fast technique. Its feature is that not need any certain testing samples just needs a component of scrap.
- Its main drawback is that not have features to identify material in a positive way; for positive identification, chemical analysis is used.
- Its other disadvantage is that it also affects tested material.
- The use of spark testing for tool rooms, machine shops, and foundries also.
Spark Testing Process
- The bench grinder is used for making sparks, but its usage is a difficult process; instead, that portable grinder is used.
- • The grinding wheel needed to have enough surface velocity for both bench grinders, about 23 m/s, but was set in the range of 38 and 58 m/s.
- The structure of the wheel is hard and coarse, so aluminum oxide is used. Testing part set in area where there is not bright light colliding on users’ eyes.
- • The grinder wheel and souring area needed to be dark so sparks were easy to observe.
- • The testing sample is touched in a light way with a grinding wheel for spark generation.
- The main features for spark are color, volume, type of spark, and also length. Length is based on pressure applied to the grinding wheel.
- Some methods used for the process are explained here.
Compressed air method
- It is not very common to produce sparks by heating a sample to red heat and after that applying compressed air to the material. The compressed air provides oxygen for the ignition of materials and provides a spark.
- That process is highly accurate compared to the use of a grinder since it provides a sample of length as a sample.
- Compressed air is given at the same pressure. It is helpful for spark checking in a reliable way.
Automated spark testing
- Automated spark testing is used for removing the use of operator skills and services through providing reliability. The system works based on spectroscopy, spectrometry, and some other processes for observing sparks emitted.
- It is found that in this process the difference between 2 materials that release sparks is differentiated for our eyes.
Spark Features
Wrought iron
- Wrought iron sparks emitted in straight lines. The back side of Sparks is wider close to the end and like a leaf design.
Mild steel
- Mild steel sparks are, like wrong irons, with small forks and lengths that can be different. Spark is white.
Medium-carbon steel
- It is more forking as compared to mild steel and comes with different types of spark length, close to the grinding wheel.
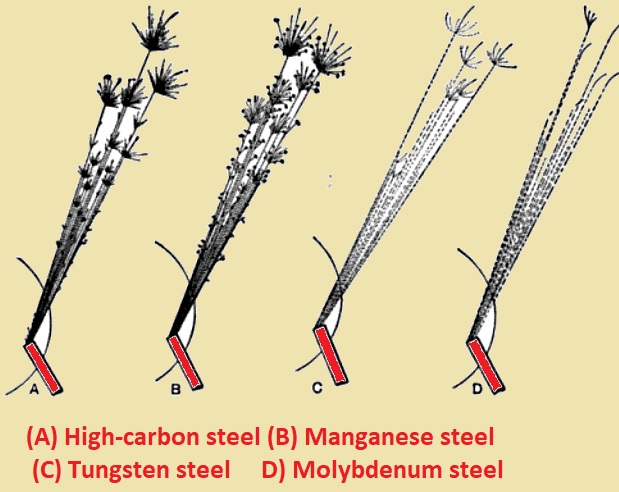
High-carbon steel
- High carbon steel comes with a bushy spark design that originates at the grinding wheel. The spark has low brightness compared to medium-carbon steel ones.
Manganese steel
- Manganese steel comes with medium-length sparks that are double-forked before finishing.
High-speed steel
- It comes with a faint red spark that sparks at the tip.
300-series stainless steel
- This type of spark is not as highly dense as carbon steel sparks are, not for long, and it has an orange color.
310-series stainless steel
- This type of spark is small in size and thin as compared to 300 series sparks. It is red to orange in color and does not have a fork.
400-series stainless steel
- This spark is like 300 series sparks but comes with a longer design and has a fork that ends at the sparks.
Cast iron
- Cast iron comes with short sparks that started at the grinding wheel.
Nickel and cobalt high-temperature alloys
- It is thin and small in size, is dark red, and does not have a fork.
Cemented carbide
- It comes with a spark in a range of 3 inches that is dark red in color and does not have a fork.
Spark Color
- The spark color is based on temperature, and its temperature is based on the energy of the metallic chunk. If a grinding wheel is spinning with a certain energy, it uses energy for removing a small part of steel on a larger testing component.
- That energy is removed from the system, and it comes with low remaining energy for sending that speck flying in the air.
- Here we observe that harder metals needed more energy for separating, which produced sparks with small energy and a redder color.
Spark Length
- The spark length also lies on energy in the spark and how quickly it cools in air. Sparks having a high surface area get cool faster as compared to sparks of the same weight with a low surface area. Increases in carbon also reduce the length of the spark.
Spark Forking
- In some conditions sparks split in midair, such as fire working that causes magnificent outcomes. In some conditions a single spark forks many times. The oxidation of steel on the surface of metal generated carbon dioxide as a result of a byproduct.
- If it occurs in a spark, pressure increases until the complete mass explodes.
- That creation of carbon dioxide is based on unequal distribution of carbon in the original steel.
FAQs
What are the uses of the spark test?
- • The spark testing process is used for finding types of ferrous materials. It is used for taking metallic components, like scrap, and applying a grinding wheel to check for released sparks.
Can we identify metal with the help of sparks?
- As a result of the spark test, a spark is produced from the metallic component through grinding against the wheel. Color, length, and type of spark can define types of metal.
What metal produces more sparks?
- Products made with carbon steel, cast iron, stainless steel, or wrought iron produce more sparks. Nonferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, brass, silver, and lead also produce more sparks.
What metal produces red sparks?
- High-speed steel comes with a faint red spark that has a spark on the tip. These sparks have less density as compared to carbon steel sparks, are orange in color, and do not fork.
What is the working of a spark tester?
- The ignition spark tester is a tool that is used for finding electrical current reaching the spark plug in the engine. The current is used for detonating the air and fuel mixture in the engine cylinder for generating power.
What are the disadvantages of spark testing?
- Spark discharge is nonlethal; direct connection with discharge produces an involuntary reaction that causes any damage. Stored high-voltage charge on a tested glass surface also discharges for operator in an involuntary reaction.
What is the function of a spark tester?
- Spark testing is used for low-voltage insulations and medium voltage non conducting jackets. The test unit produces electrical clouds about cables that are in high-frequency AC units, shown like blue coronas about cables.
Why do cables spark?
- The spark is produced if there is a potential difference between two wires. The spark exists since current jumps jumps from one wire to another for charge equalization on both wires and reduces electrical potential between them to zero.