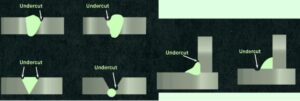
Undercut in welding is defined as a groove that makes the edge of a welding joint. It occurs when molten metal does not completely fill in the weld groove, making a nonuniform or incomplete surface. These errors weaken the weld and create chances for cracking or breaking. The presence of undercut on the surface is easily detectable. The undercut is seen as a small trench over weld bead edges. Here we will cover details for undercut in welding creation and how to avoid it.
What Is an Undercut?
- In welding, undercut occurs when the weld reduces the cross-sectional thickness of the base metal. This error affects the strength of the weld and the working component.
- This error is the result of high current, resulting in joint edges melting and draining into the weld that makes a drain-like impression over the weld length.
- It also occurs due to improper welding techniques that do not deposit filler metal over weld edges.
- Undercut also occurs if filler metal is not used accurately, since it makes high temperature gradients between the middle of the weld and the edges.
- Some other causes for undercut are a small electrode angle, high arc length, dampened electrode, and slow speed.
- Undercut reduces the structural quality of the welded joint and causes cracks and damage.
Acceptable Amount of Undercut
- The acceptable amount of undercut can be different, but if you have a 1/16-inch-deep undercut, that is not accepted based on the AWS D1.1 Code.
- • An undercut of less than 0.5 mm is normally safe to use. For measuring undercut, the upper limit is 1/16 inches and the lower limit is 1/32 inches.
- In this range welding inspection, check the total length of the undercut; if it is higher than 2 inches in a 12-inch part, it is not accepted.
Read more:What Butt Welding: Features, Process, Types, Joints & Uses
Causes of Undercut in Welding
- The main causes of undercut in welding are the use of wrong welding features, faulty electrodes and shielding gas, and bad welding techniques. Each factor helps to make an undercut that causes weak joints and faults in welds. The main causes for welding undercut are as follows.
Wrong welding features
If welding features are not good, that causes undercuts.
High Current
- Current defines how much energy goes into the weld. The base metal melts higher than the requirements if it is high and makes a deep weld pool. The high additional liquefied metal moves away from the boundary to the tool. That makes a crater at the edges.
High Travel Speed
- High electrode travelling speed and undercut are related to each other. If travel speed is high, the electrode moves from the weld pool. In this result, there was not enough molten metal for spreading before it became solid.
- Moving the electrode away quickly from the source helps metal to freeze in the middle of the weld pool. That makes an undercut over the weld edges.
High Arc Voltage
- Voltage also shows total heat input of weld. When voltage increases, more heat goes to the weld zone, and as a result, more metal melts.
- High heat produces a larger cavity than the required size that is not completely filled. That converted into an undercut on the weld side due to the absence of filler materials.
Wrong Electrode & Shielding Gas
Undercutting based on use of electrode and shielding gas. These factors define the working of the weld pool and undercutting.
Electrode Material
- Filler material and base metal needed to have the same thermal features. If there is a difference between them, it can change the chances of head flow in the weld zone.
- It causes premature solidification but also affects wetting features of metals. That causes the creation of an undercut.
Electrode Angle
- Working angle is also important for making error-free welds. If you have an improper electrode angle, that causes uneven heat input on the welding area. On edges, overheating melts the weld pool and makes an undercut.
Electrode Size
- The use of accurate electrode size is also important. If it is not according to size, extra filler is added into the pool and gathers in the middle part of the groove as a result of high surface tension.
- Based on the larger stick diameter, heat input is also highly scattered. That makes undercutting. A small electrode also causes errors; filler metal is not good for filling the joint, resulting in an undercut at the bead edge.
Wrong Shielding Gas
- Undercut also occurs if there are wrong shielding gases or pressure not regulated according to welding demands. Gas does not protect the weld pool from the environment. If air makes a reaction with molten melt, that affects wetting features and heat transfer efficiency. As a result, undercutting occurs.
Welding Technique
Weaving Technique
- Weaving method used for welding work. If you do not have proper welding experience, that causes undercut at the weave pattern that is close to the groove fillet edges.
- It occurs due to the welder faultily passing the electrode through joint edges. This high-speed process makes for high traveling speed and helps premature cooling of the molten pool.
- So move fast over the center and stop on the edges of the weave flow.
Arc Length
- Arc length also causes undercutting problems. It occurs due to the long arc not providing smooth heat energy distribution for the weld zone.
- So some parts get more heat and melt accurately, and other parts become solid in a short time due to low heat.
- This imbalance causes undercutting.
How to Prevent Undercut in Welding
Follow these points for undercut prevention in welding.
- Use a low current value if there are constant undercuts. Since low or right current amount minimizes overheating for accurate fusion
- Use an accurate voltage knob that avoids undercuts and makes a uniform finish and even bead profile.
- Perform the welding process slowly to provide proper time for fusion and early solidification.
- Before using filler materials for welding, get details or consultation with an experienced welder.
- Set angle that deposits filler in a uniform way in the weld pool For this, check each side of the bead and find differences.
- Use proper electrode size and accurate electrode fill groove and provide smooth energy.
- Use accurate gas mixture for welding purposes.
- Perform the weaving process with time-taking at edges for providing accurate fusion at high-risk locations.
- Set arc length accurately; if you have faulty arc length, extra spatter or resistance occurs for motion. Indicators are used for setting this issue and maintaining a constant value during welding.
Types of Undercut
External Undercut
- External undercut occurs at weld toe. In fillet welding, it is seen on the front of the joint that is seen at the time of welding. External undercuts are common, as the front surface is close to the weld gun.
Internal Undercut
- Internal undercut made on lower part of butt joint. It is at the root of the weldment, which is also called the root undercut.
Read also: Mig Vs Tig Welding: Basic Differences
Why Is Undercut a Problem?
Undercuts cause bad effects for structures and also some visual problems that affect weld quality. Based on welding processes and techniques, these issues can cause different errors. Some problems related to undercutting are as follows.
Affect weld strength
- Undercuts minimize the metal fused with each other and also weaken the strength and load-bearing features of the weld.
Cracking:
- Undercutting also causes cracks in the weld as a result of stress on the edges.
Corrosion
- The exposed base metal in the undercut has chances of corrosion that affect the quality of the weld joint.
Brittle Welds
- If undercuts occur in high-stress locations, it causes brittle and weak welds that are easy to damage.
FAQs
What is the reason for undercut in welding?
- Undercut occurs due to many causes, such as high heat from high-current and high-voltage devices.
- Travel speed is high; as a result, the electrode moves away from the weld pool badly, causing undercut. If edges are not properly prepared, dust on the welding surface blocks accurate fusion that causes undercutting.
Does undercut weaken a weld?
- Yes, undercuts make weak structural quality of joints. In some conditions this low thickness gets damaged in case of load.
- Undercut also has a bad effect on the strength of joints through water and particle trapping, which results in corrosion.
How to control undercut welding?
- Use accurate or required voltage value. Sets high arc length and reduces arc distance.
- Avoid bad torch or electrode angles.
- Welding speed set at a low value.
What is the difference between undercut and underfill?
- Both are common types of error in welding; undercuts occur for grooves over the edge of the weld that reduce weld strength and cause cracks.
- Underfill occurs if there is not accurate weld material, which causes incomplete fusion and affects strength.
Can damage from an undercut be fixed?
- External undercut can be fixed with just adding a pass where the undercut exists. It is needed to clean the undercut and grid bit to provide space for depositing a pass free from fusion error. High grinding, which removes high weld or base materials, causes undercut. So set a limit for grinding at mining value.
Conclusion
Undercuts are difficult to avoid. By following different parameters and techniques, we can avoid them in welding. For handling this error, get the services of a professional with the latest method for controlling undercutting.