The workings of the car engine are like those of the human heart. Humans move by breathing through their hearts, and cars operate through their engines. The main function of the engine is to transform heat into gases in a burning form that move the alloy wheels. There are different parts of the engine, but the cylinder head and cylinder block are very important parts of the car engine. Since the cylinder block comes with different components of the engine, such as cylinders, pistons, and the crankshaft.
Many parts of the engine have their own workings and features. We will cover all parts here.
What is a car engine?
- The car engine is called the heart of the car. It comes with a certain process of working that converts thermal energy as a result of the combustion of gasoline, into kinetic energy that is used for moving the wheels.
- This process started with a spark that ignited petrol vapor and air. This mixture burns as a result of flame creation and makes an internal combustion engine.
- Due to the burning of the fuel mixture, expansion occurs, and pressure is produced that helps to move the car.
- The engine has two main parts: the cylinder block, which controls the movement of internal rotating parts, and the second component is the cylinder head.
- There is a path that exists at the head of the cylinder where air, fuel, and gas move from the inner side to the outer side of the cylinder, controlled through a valve connected to the head of the cylinder.
- According to the pressure in the cylinder, fuel and gas are moved in and out of the cylinder.
- The engine block comes with a crankshaft block, and it converts the linear movement of the piston into rotational motion over the crankshaft.
Car Engine Working
- The internal combustion engine converts energy obtained from gasoline burning into torque. This torque moves the wheels, which helps the car move forward.
- The working of the engine is like the working principle of Ford or Ferrari, but different for the older two-stroke Saab.
- Engines come with pistons that move up and down in hollow metallic tubes; that is known as cylinders.
- Pistons connected through rods with the crankshaft move up and down to spin the engine crankshaft. That is, as our legs give power to bike driver wheels.
- Whether you are driving which type of vehicle, the engine comes with 2 to 12 cylinders, and each comes with pistons that move up and down.
How does Engine Power Produce?
Car engine’s work is based on a four-stroke combustion cycle that has four parts explained here.
Four Stroke Cycle
Intake Stroke
- • The intake stroke comes with an open inlet valve and a closed outlet valve. Negative pressure is created in the cylinder when the piston moves downward, and as a result, the expanding volume increases.
Compression Stroke
- The compressor chamber compresses the air-fuel mixture to provide ignition. The inlet of the engine and the outlet valve are closed, and the piston moves upward.
Power Stroke
- Spark plugs have a firing process; the combustion stroke applies downward force to position and move the crankshaft; as a result, the car moves. The piston also moves downward in the cylinder bore from top dead corner to lower dead center. As a result, inlet and outlet valves get closed.
Exhaust Stroke
- Cylinder bore shows movement from position from TDC to BDC. The movement is produced with a power stroke that stops the crankshaft from moving. But the outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is closed.
- The exhaust gases move out of the cylinder, and the piston starts the intake stroke.
- Gas, when burned, moves to the catalytic converter. Also, gas is clean and moves to the buffer.
- Clean gas is released through the pipeline.
- There is a 20 percent efficiency for gasoline engines for transforming fuel into mechanical energy and 15 percent for energy wheels.
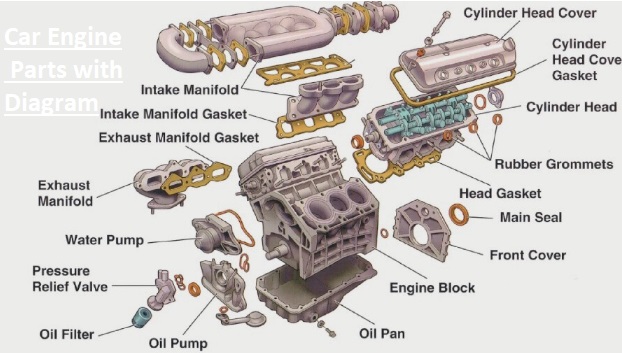
Car Engine Parts with Diagram
Different parts of the engine of a car have certain functions. An internal combustion engine comes with about 200 parts, and most of them are listed here.
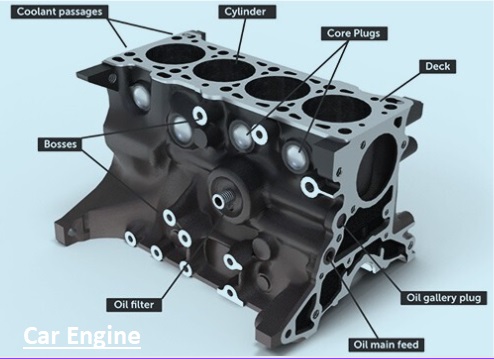
Engine block
- The engine block is an important part of the engine. This part of the engine comes with different holes that configure the cylinder and control water and oil movement to make engine coolant, and some are used for lubricant flow. Oil flow is narrow compared to water flow.
- The main parts of the engine block are the positions of the crankshaft and camshaft, and depending on the vehicle, it has 4 to 12 cylinders that are configured in line, in a V shape, or in a flat design.
- All parts of the engine are configured to the engine block. The combustion process occurs in a block.
Piston.
- It is a cylindrical-shaped component with a flat surface on the upper part. Its working is to transform energy produced from combustion to the crankshaft.
- As a result of each rotation of the crankshaft, the piston moves up and down in the cylinder.
- In 60 seconds, an engineer working at 1250 RPM moves the piston up and down 2500 times.
- Piston rings are on the lower side of the piston, which increases compression and reduces the friction of the piston to the cylinder.
Crankshaft
- The backbone crankshaft is compatible with the internal combustion engine. Its working is to control the movement of the crankshaft and change the motion direction from linear to rotational.
- Wheels of the car operated with rotational power generated with the motion of pistons that move crankcases connected below the engine block.
- Crankshaft control lower component of engine block. Crankshaft made with steel for managing tensile strength.
- It has features to control high tension at the time of driving and reduces oscillation space that is important for the rotation of the crankshaft. The design of the crankshaft is like one unit design.
- The crankshaft is connected with the engine with the use of two larger-sized bearings at both ends. Flywheel connected with crankshafts through use of a small disc or clutch.
- Rotational motion of the crankshaft is provided through the gearbox at the time of driving to the wheels and helps to move the car.
Camshaft
- The car model defines the location of the camshaft, which means it lies at the engine block or cylinder heads.
- In modern cars, it is connected in the cylinder heads, and it is also called DOHC or Dual Overhead Camshaft. It is compatible with bearings that are lubricated with oil.
- The camshaft works to handle a certain operation sequence if the valves are closed or open. It also gets rotation from the crankshaft and transforms it into vertical motion that regulates the lifters for moving pushrods and rockers.
Piston Rings
- The main working is to provide a sealing effect for the position and cylinder. It avoids leaking engine combustion gas, crosses the piston, and reduces friction of the piston.
- Piston rings are created with cast iron and alloy cast iron. There are two main types of rings: compressor rings and oil control rings.
- Compressor rings send heat from the position to the cylinder liner, and it is configured into the top grooves of the piston.
- The main working of compressor rings is to reduce side thrust over the position that causes changes.
- Oil control rings are used for lubrication between the cylinder and piston and lie below the pressure rings.
Connecting Rod
- The connecting rod makes the connection of the piston with the crankshaft through the piston pin and crank pin. The connecting rod converts the piston linear motion into the rotation motion of the crankshaft. As a result, the level arm converts the motion from one end to another.
- One end is called the big end, which is configured with the crankshaft, and the other end is called the small end, which is configured with the piston.
- Connection rod made with the use of low carbon steel in case of a small-sized engine made with cast aluminum alloy. For manufacturing, heat treatment and forging are used.
Cylinder Head
- • The cylinder head is connected with the engine block through lots and sealed with a head gasket.
- This structure comes with different components such as valve springs, lifters, pushrods, and camshafts. It has a path for airflow into the cylinder at the time of the intake stroke and releases used air at the time of the exhaust stroke.
Combustion Chamber
- The combustion chamber is an important part where the explosion occurs. Here, fuel, current, and air mix to provide power to the pistons of the motors, which helps the car move. The main components of the combustion chamber are the piston, the cylinder, and the cylinder head. The complete design makes the combustion chamber. A cylinder is a wall of a chamber with the piston top on top, and the cylinder head is the upper part of the combustion chamber.
Timing Belt/Chain
- The timing belt, also called camblet, is a component of the engine that operates to synchronize both crankshaft and camshaft movement by providing valve openings and closings in cylinders for accurate time intervals at the time of intake and exhaust strokes.
- For the interference engine, the timing belt is used to make sure that the piston does not strike the valve. The timing belt is a toothed belt; the drive belt has teeth on the internal design.
- The timing chain is called a roller or bicycle chain.
- The belt comes with high-strength rubber and teeth that control the pulley connected at the camshaft and crankshaft.
Engine Valves
- The main part working is to control air and fuel and release exhaust gases from the cylinder head when the engine is working.
- The working of the valve does not have any complicated process; just the cam pushes the valve into the cylinder where it scrubs over the spring, so opening the valve allows gases to flow, and as a result, the spring closes the valve.
Spark Plugs
- Each cylinder comes with spark plugs. Spark plugs are a component of car engines that control the air mixture with fuel, providing an explosion to the engine.
- For the production of an explosion, the AIX fuel mixture was ignited before the compression stroke, so a spark plug was used. In the latest vehicles, high voltage is needed for the spark generated with the ignition coil and the move to the combustion chamber.
- The spark plug comes with a threaded metallic sheath having a central electrode. The ceramic insulator covers the internal electrode that has a resistor. The central electrode makes a connection with the wire to heavy insulation with output points of the ignition coil or a magneto.
- Due to the ignition coil and magneto being turned on, the spark plug metallic casing is connected with the engine cylinder head that is grounded.
Intake manifold
- • The intake manifold is part of the engine that gets airflow and separates it over cylinders. The intake manifold comes with the throttle valve and other components.
- The intake manifold comes with different components in different engines, like V6 and V8 engines.
- It also provides motion of mixture that defines the working of the engine.
Spark Plug
- The spark plug is a device that is employed for producing a spark between two electrodes and igniting a combustible mixture in the combustion chamber. It has features to handle changes in pressure and temperature.
- Its main working is to control high potential from the ignition system to the combustion chamber. The spark plug also has a certain gap where a spark is generated with the application of high voltage for ignition of fuel in CC.
Poppet Valves:
- The poppet valve is a high-speed operation and high-flow valve. It is connected with pressure control devices and provides directional control flow.
- • The poppet valve is made with a valve stem and metallic flat disks. This valve comes with a mushroom head design that is used for opening and closing intake and exhaust ports in the cylinder head.
Carburetor
- The creation of a combustible fuel-air mixture externally is called carburation. The carburetor is a component that atomizes fuel and mixes it with air. The carburetor is employed for petrol engines that are mixing modules for providing engine-to-air-fuel mixtures.
- It also atomizes fuel and combines it with air for changing proportions for fulfilling the automobile engine conditions. It is also used for reserving fuel supply and painting a constant head fuel.
Catalytic Converter:
- Catalytic converter used to change bad gases from engine emissions into safe conditions such as steam. It is connected at the bottom of the auto vehicle, where two pipes are coming out, and the converter uses two pipes and a catalyst at the process of making gases to safely release them.
- The catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that uses chemical reactions and redox reactions and reduces toxic pollutants and gases from exhaust gases in IC engines.